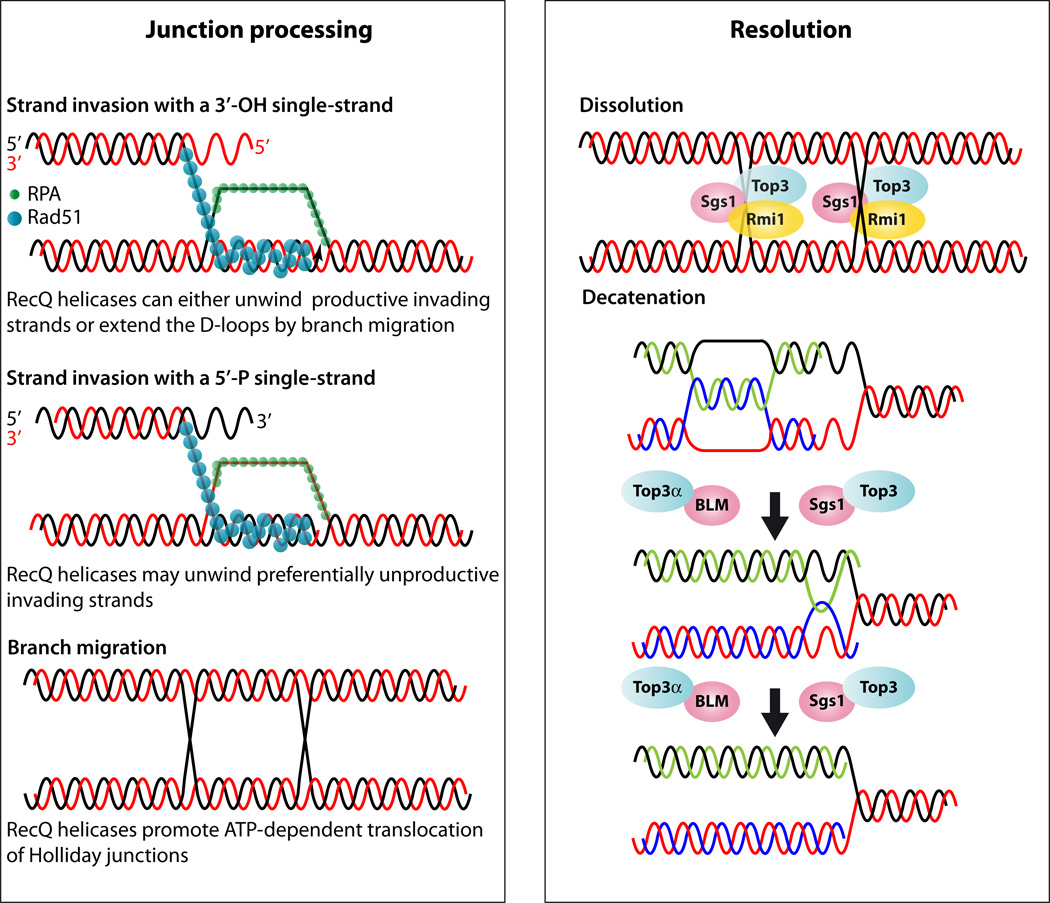
Figure 4.
Model for RecQ function during junction processing and resolution. Junction processing: The Rad52 group of proteins recruits Rad51 and displaces RPA leading to Rad51 filament formation. Rad51 filaments perform homology search and strand invasion leading to D-loop formation followed by branch migration. Rad51 coated DNA can invade using 5’ or 3’ DNA ends; however, only the 3’ invading end is proficient for homologous recombination. The RecQ proteins can unwind the 5’ end and thus abort the unproductive reaction but also the 3’ end after it is extended to promote synthesis dependent strand annealing (not shown). Alternatively, second end capture of the homologous chromosome can lead to double Holliday junction formation (dHJ). The RecQ proteins function by promoting translocation and branch migration of dHJs. Resolution: Dissolution of dHJs utilize the Sgs1-Top3-Rmi1/BLM-TOP3α-RMI1(BLAP75) complex. In the figure the yeast proteins are shown bound to each HJ and if they move toward each other dissolution can occur. However, the precise biochemical reaction is not known. During DNA replication, hemicatenenes are thought to form behind the replication fork (17). In vitromaximal decatenation of this structure is achieved when Rmi1 and Rmi2 are added to the reaction.