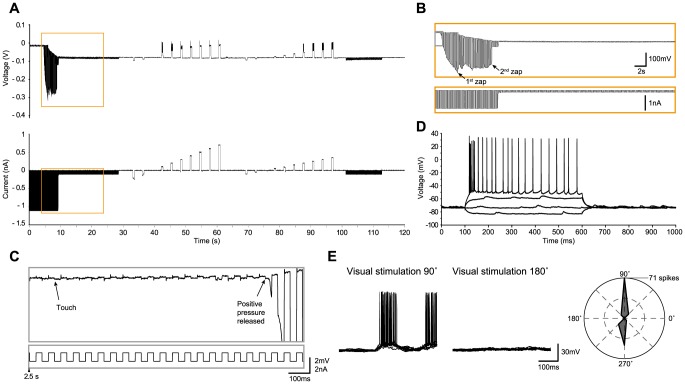
Figure 2. Regular-spiking neuron in cat visual cortex in vivo recorded with the TZ method.
(A) Voltage and current recordings under current clamp mode during the approach to the neuron, detection of contact (“touch”; at ∼6 seconds), release of pressure with immediate seal formation, electroporation of the membrane and establishment of whole-cell access (“zap”), and initial measures of the voltage response to current steps. (B–C), expanded traces from (A) highlighting the access to the whole-cell configuration. (B) corresponds to the region marked by the orange square in (A), and (C) corresponds to the region marked by the grey square in (B). The “touch” is characterized by a small increase in the electrode resistance (C). The positive pressure in the pipette is released within a second after the touch, followed by an immediate increase in the electrode resistance as the seal spontaneously forms. A first “zap” occurs within about one second (B), followed by a second “zap” which results in the whole-cell configuration, evidenced by the much smaller voltage deflections, and the hyperpolarization of the voltage envelope as the cell's resting potential establishes a DC bias. At this point the current pulses are typically set to 100 pA, switching polarity as necessary to estimate and compensate for Ra. (D) Voltage responses to current steps (−100, 0, 150 and 250 pA), with the response to 250 pA showing a regular-spiking firing pattern. (E) Left – Examples of preferred (180°) and non-preferred (90°) responses (10 trials overlaid) to a moving sinusoidal grating (4 Hz, 100% contrast, 0.5 second duration). Right - Total spike count over the 10 trials as a function of stimulus direction, showing that this neuron is strongly tuned to stimulus orientation and modestly tuned to stimulus direction. The on-line corrected Ra for this recording was 24 MΩ, which was subsequently corrected off-line to 21 MΩ. The input resistance was 102 MΩ, giving a relative Ra of 0.21.