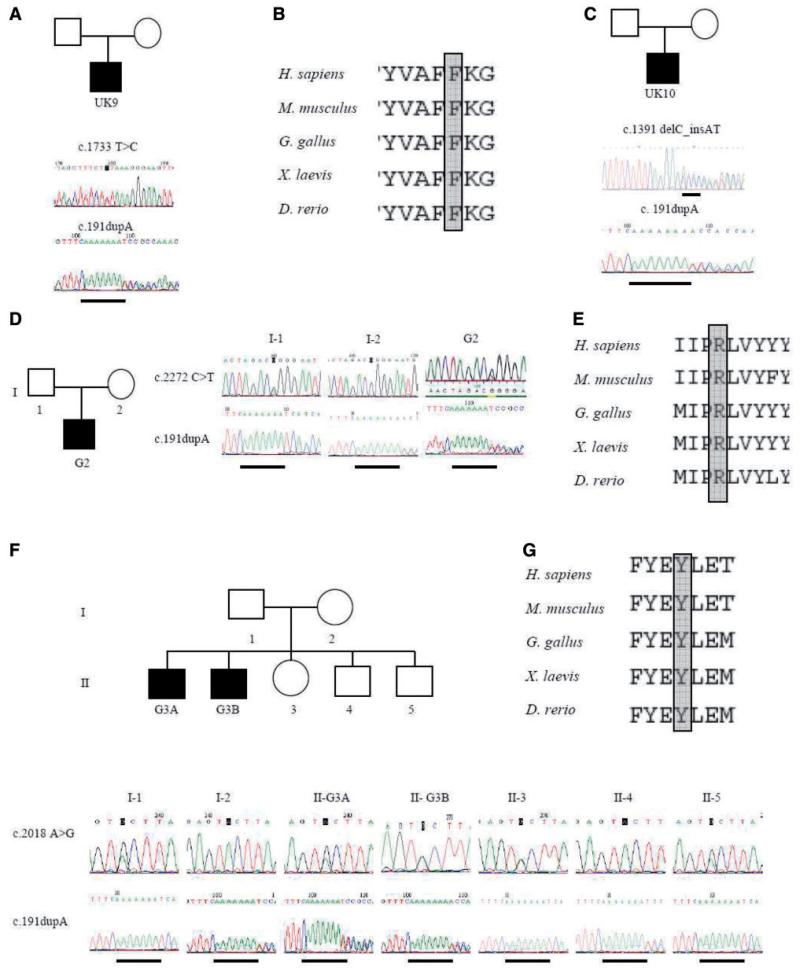
Figure 1.
Identification of ANO5 mutations in UK and German families. Electrophoretograms of genomic DNA sequencing show heterozygous c.1733T > C p.Phe578Ser and c.191dupA mutations in patient UK9 (A), and protein alignment of residue Phe578 (B). Heterozygous c.1391delC_insAT and c.191dupA mutations in patient UK10 (C). Electrophoretograms of genomic DNA sequencing of patient G2 show heterozygous c.2272C > T (p.Arg758Cys) and c.191dupA mutations (D). His unaffected father carries the c.2272C > T mutation and unaffected mother carries the c.191dupA mutation. Protein alignment of residue Arg758 (E). Electrophoretograms of genomic DNA sequencing show heterozygous c.2018 A > G (p.Tyr673Cys) and c.191dupA mutations in patient G3A and G3B (F). Unaffected family members are carriers of either the c.2018A > G mutation (I-1, II-3, II-5) or for the c.191dupA mutation (I-2, II-4). Protein alignment of residue Tyr693 (G).