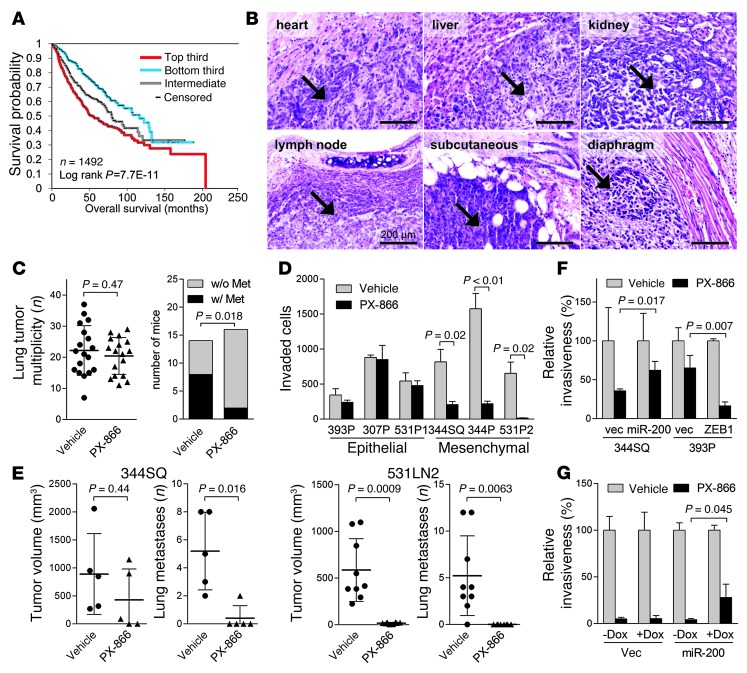
Figure 1. Mesenchymal lung adenocarcinoma cells are sensitive to PX-866.
(A) Survival analysis of lung cancer patients comparing differences in risk between tumors according to degree of manifestation of a PI3K/mTOR inhibitor–regulated transcriptional signature. Kaplan-Meier plot compares the top, bottom, and middle thirds of the T-score values. (B) H&E staining of metastatic tumors (arrows) in KP mice. Scale bars: 200 μm. (C) Numbers (n) of visible lung tumors (scatter plot) and mice with (w/) or without (w/o) histologically documented metastases (Met) (bar graph). Metastasis incidence P value (Fisher’s exact test). (D) Invasion assays. In a single experiment, invasive KP cells were quantified after a 24-hour incubation with PX-866 or vehicle. Mean ± SD from triplicate samples. (E) Scatter plots of primary tumor volume and numbers of visible lung metastases in a single experiment in which syngeneic mice were injected with 344SQ cells (5 mice per cohort) or 531LN2 cells (9 mice per cohort) and then treated with PX-866 or vehicle. Mean ± SD was calculated for each cohort. (F and G) Invasion assays. Invasive KP cells (F) and H1299 cells (G) were quantified in the presence or absence of PX-866. H1299 cells were treated with (+) or without (–) doxycycline (Dox) (1 μg/ml) to induce expression of the miR-200b/a/429 construct. Mean ± SD from triplicate samples. vec, vector.