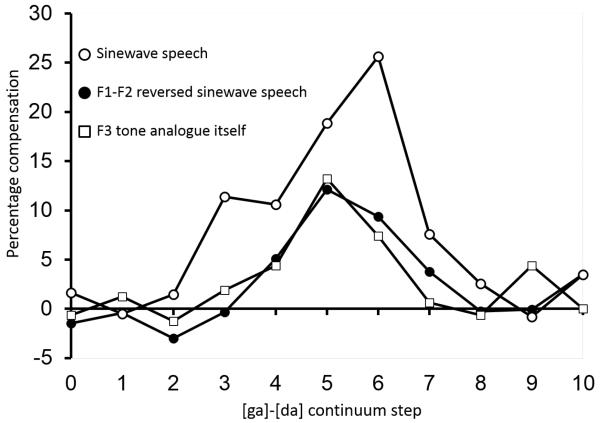
Figure 3.
A comparison of the average compensation (expressed as the % “g” responses to the [al] analogue - % g responses to [aɹ] analogue, at each step, for each subject) produced by sinewave speech (open circles), selectively-reversed sinewave speech (filled circles) in Experiment 2 and F3 sinewave in isolation (open squares) in Viswanathan et al. (2009, Experiment 2). Even though three conditions all contain identical F3 analogues, sinewave speech produces robust effect that are stronger than the other two conditions which themselves produce comparable effects. These data suggest that the strong effects of the sinewave speech precursors are due to their spectro-temporal acoustic structure rather than their F3 offsets.