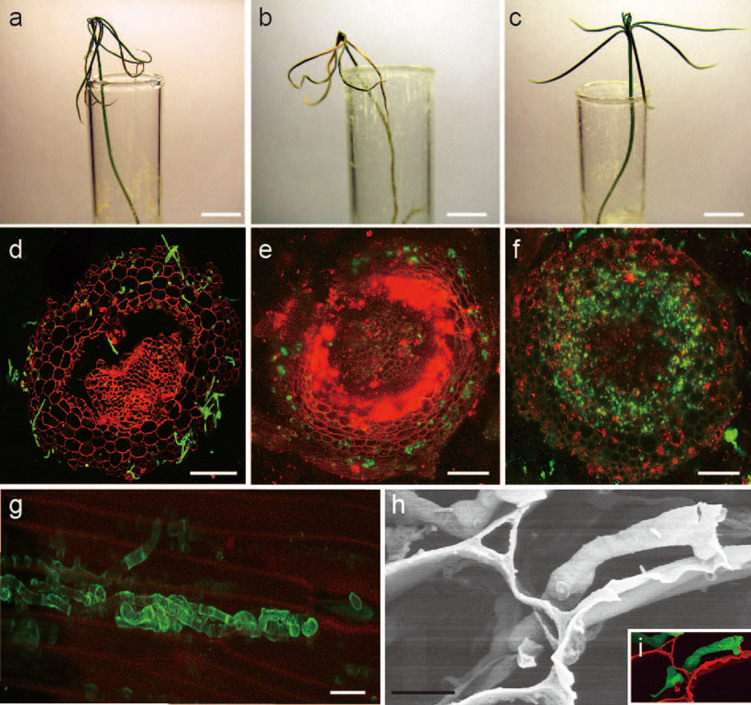
Figure 1. Pathogenic interactions between N. crassa and Scots pine seedlings.
Scots pine seedlings were inoculated with N. crassa (a), H. annosum (b), and control (c). (d) Transverse section of Scots pine root inoculated with N. crassa. Plant cell walls were stained with PI, and fungal hyphae were labeled with WGA. (e and f) Transverse sections of Scots pine roots inoculated with N. crassa FGSC 10589. GFP images were obtained by staining with FM4-64 at different stages of infection from 3 (e) to 5 (f) weeks post inoculation (wpi). (g) Image of N. crassa hyphae stained with WGA within host plant cells. (h) SEM image of N. crassa hyphae growing from one plant cell to another. (i) Colored SEM image, red and green indicate plant cell wall and N. crassa hyphae, respectively. Bars = 1 cm (a–c); 100 μm (d, e, and f); 10 μm (g); 5 μm (h). N. crassa strains used in a, d, g, h, and i was FGSC 2489.