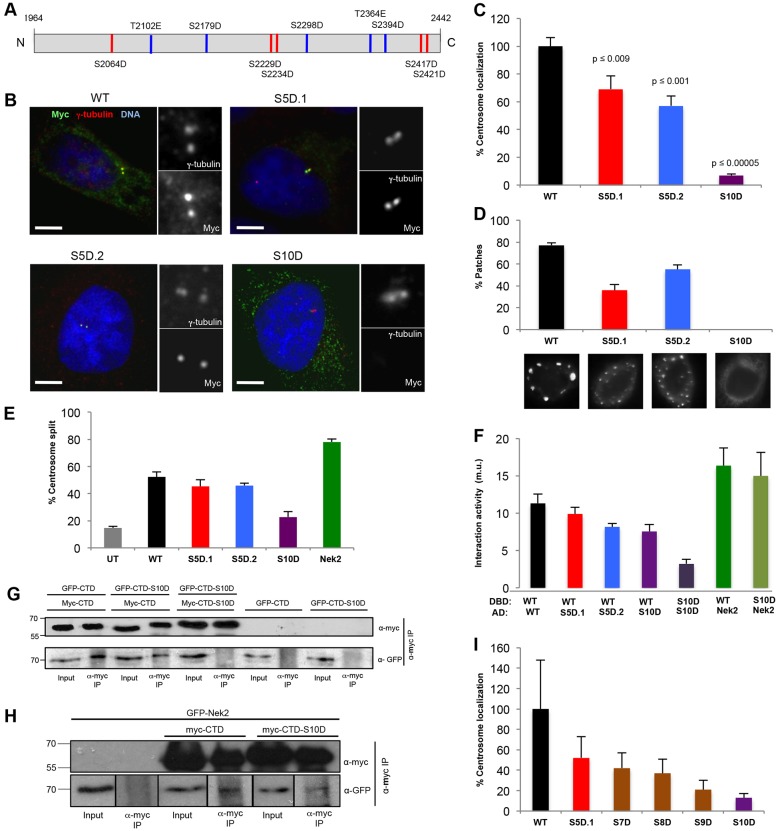
Fig. 3.
Phosphomimetic mutations prevent C-Nap1-CTD oligomerization and centrosome localization. (A) Schematic diagram showing the ten phosphorylation sites mutated in the Myc-tagged C-Nap1-CTD-S10D mutant. Red, sites mutated in the S5D.1 mutant; blue, sites mutated in the S5D.2 mutant. (B) U2OS cells were transfected for 24 hours with the Myc-tagged C-Nap1-CTD constructs indicated and stained with antibodies against γ-tubulin (red) and Myc (green), and with Hoechst 33342 to visualize DNA (blue). Magnified views of centrosomes are shown. Scale bars: 5 µm. (C) The percentage of transfected cells in which the recombinant protein was detected at the centrosome is shown (n = 50). P-values for each construct compared with the wild type (WT) are indicated (Student's t-test). (D) The percentage of transfected cells positive for large patches of recombinant protein, together with representative images of each construct stained with antibodies against Myc, is shown (n = 30). (E) The percentage of transfected cells in which the two centrosomes were split (>2 µm) is indicated (n = 100). UT, untransfected cells. Cells transfected with Myc–Nek2A were used as a positive control. (F) Yeast two-hybrid assay in L40 S. cerevisiae indicating interaction activity (m.u., Miller units) between the proteins shown where the upper protein was a LexA-DBD fusion and the lower a VP16-AD fusion. (G,H) GFP–C-Nap1-CTD (G) or GFP–Nek2A (H) were coexpressed with Myc–C-Nap1-CTD or CTD-S10D in U2OS cells for 24 hours, as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) using antibodies against Myc, and inputs and immunoprecipitates were western blotted with anti-Myc and anti-GFP antibodies. Molecular mass (kDa) is indicated on the left. (I) The percentage of transfected cells in which the recombinant CTD protein was detected at the centrosome is shown (n = 50). Data in C–F and I show the mean±s.d. (at least three independent experiments).