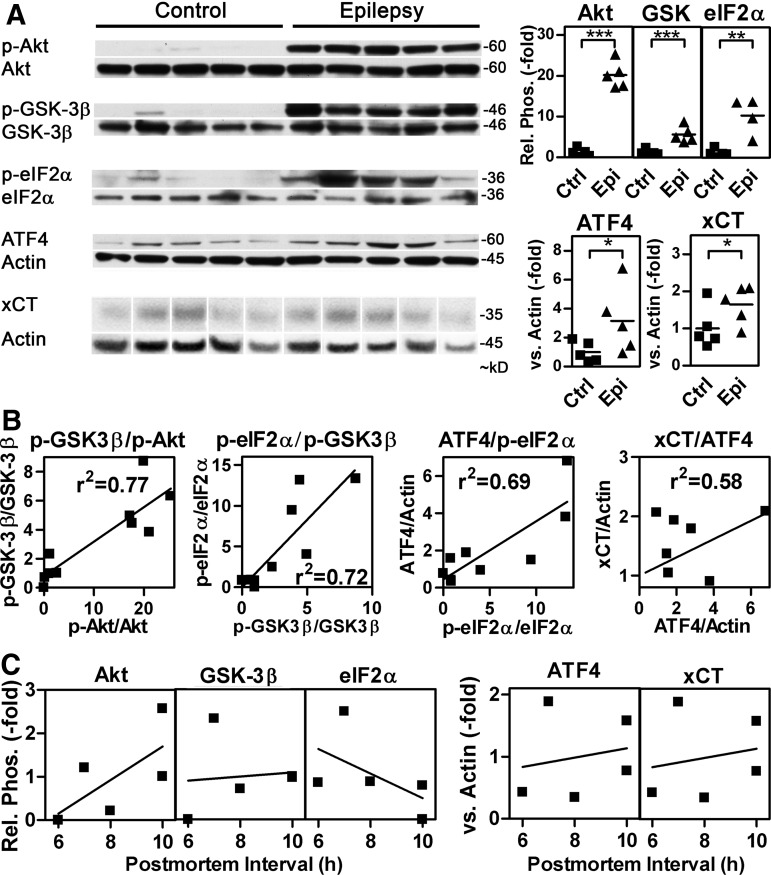
FIG. 8.
The PI3K/GSK-3β/eIF2α/ATF4/xCT pathway is activated in human epileptic hippocampal tissue. Protein extracts from surgical specimens from human epileptic hippocampi (Epilepsy) and control hippocampi (Control) were tested for the relative phosphorylation of Akt (phospho-Akt), GSK-3β (phospho-GSK-3β), and eIF2α (phospho-eIF2α) as well as ATF4 and xCT expression by Western blotting. Either antibodies that recognize the proteins irrespective of their phosphorylation state (total) or actin were used as loading controls. (A) Representative blots are shown. Longer exposures than those shown were used for the quantification of some of the samples. Graphs show the quantitative results with epileptic (Epi) compared with control (Ctrl) tissue with the mean value of the control group normalized to 1. For eIF2α phosphorylation, one sample (Epi sample 2, p-eIF2α/eIF2α=55.8) was excluded, as this value was classified as an extreme outlier (see the “Materials and Methods” section). Statistical analysis was performed by one-tailed Student's t tests, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, and *p<0.05. (B) Pair-wise linear regression of the four pairs of connected parts of the pathway across the whole group of samples (Epi sample 2 excluded). The goodness of fit is given in the graphs. The slope was significantly different from zero in all cases (GSK-3β/p-Akt, p<0.001; p-eIF2α/p-GSK-3β and ATF4/p-eIF2, p<0.01; xCT/ATF4, p<0.05). (C) Relationship of Akt, GSK-3β and elF2α phosphorylation and ATF4 and xCT expression with the postmortem interval in control hippocampi.