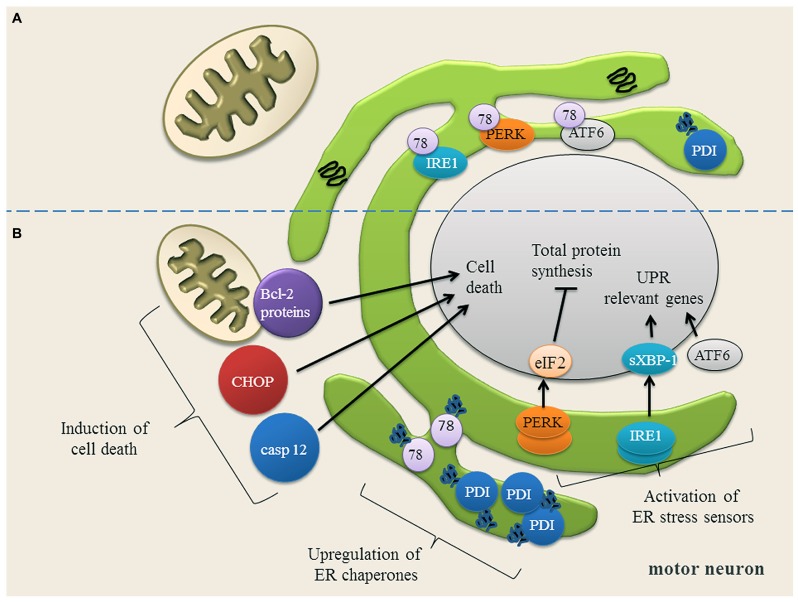
FIGURE 2.
(A) Motor neuron in a physiological state and under ER stress conditions. In motor neurons, most proteins in the ER are physiologically properly folded. The ER chaperones Grp78 (78) and protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) are moderately expressed and assist protein folding. The unfolded protein response (UPR) sensor proteins (IRE1, PERK, ATF6) are bound to Grp78 and are therefore in an inactive state. (B) Upon ER stress, Grp78 dissociates from IRE1, PERK and ATF6 resulting in the activation and up-regulation of these three UPR sensor proteins. IRE1 splices XBP-1 mRNA (sXBP-1) which up-regulates the expression of UPR relevant genes. ATF6 is transported to Golgi apparatus, where it is cleaved. The cytosolic domain of ATF6 translocates to the nucleus to activate gene expression. PERK phosphorylates eIF2α, thereby down-regulating the total protein synthesis to prevent an overload of the ER. Once the expression of ER chaperones Grp78 and PDI is induced, they bind to the misfolded proteins and try to assist their folding. If restoring of ER homeostasis fails, cell death proteins transcription factor C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) and caspase 12 (casp 12) are induced and the balance of Bcl-2 family members is disturbed, anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members are down-regulated, while pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members are up-regulated. Picture modified from (Lautenschlaeger et al., 2012).