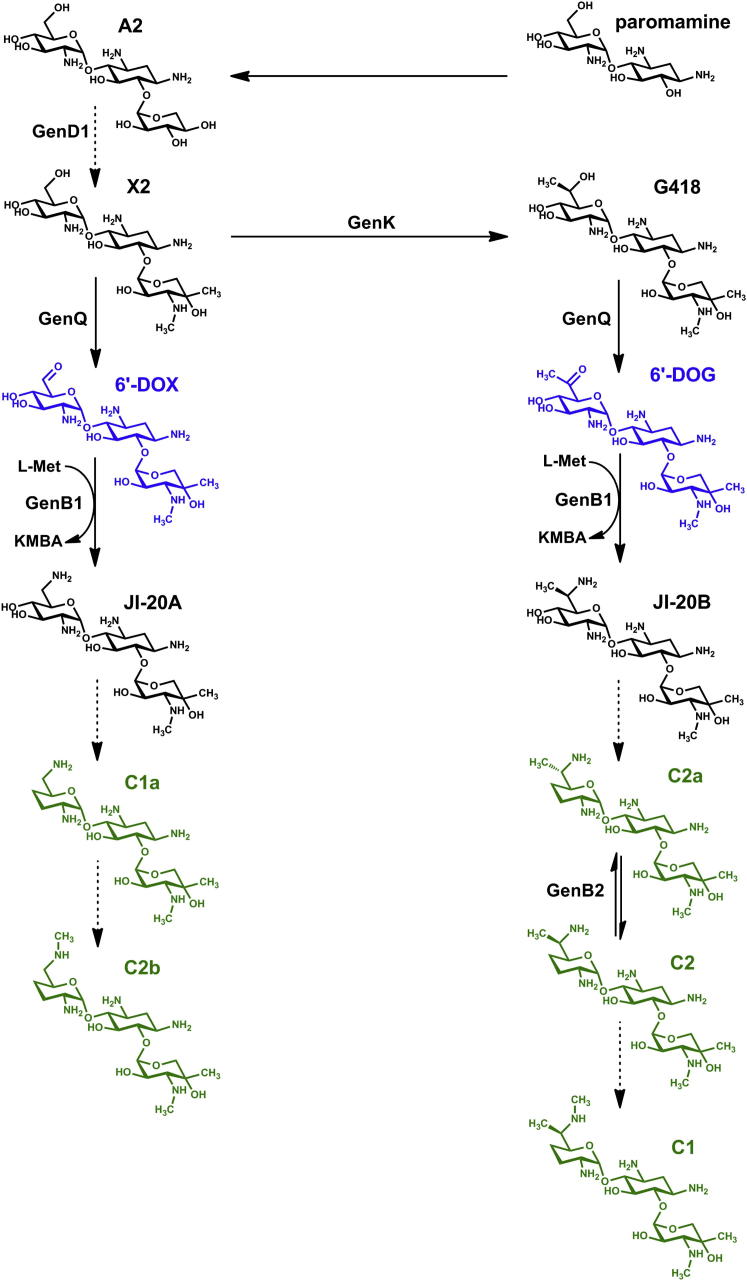
Figure 1.
Proposed Biosynthetic Pathway from Paromamine to the Gentamicin C Complex
The early steps in the pathway lead from the pseudodisaccharide paromamine to the branch point at gentamicin X2. The five main components of the clinically-used gentamicin C complex are shown in green. The proposed roles of the radical S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferases GenD1 and GenK are indicated. The role of GenK has been established by previous in vitro work. Intermediates 6′-DOX and 6′-DOG, newly-detected in this study, are shown in blue. The roles of dehydrogenase GenQ and aminotransferase GenB1 are revealed in this study, as well as the involvement of GenB3 and GenB4 in the steps from intermediates JI-20A and JI-20B to the gentamicin C complex, and of GenB2 in epimerization of gentamicin C2a to gentamicin C2. For further details see the text. KMBA, 2-keto-3-methylthiobutyric acid; 6′-DOG, 6′-dehydro-6′-oxo-G418; 6′-DOX, 6′-dehydro-6′-oxo-gentamicin X2.