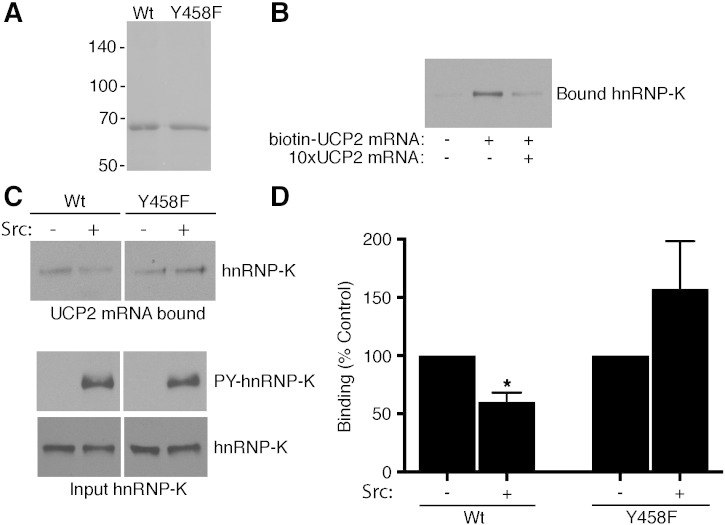
Fig. 3.
UCP2 mRNA binds purified hnRNP-K and is regulated by Src. A, Coomassie stained gel of recombinant His6-tagged wild-type hnRNP-K or Y458F hnRNP-K expressed in E. coli and purified on a nickel column. Positions of molecular mass markers are indicated in kDa. B, Binding of UCP2 mRNA and wild-type hnRNP-K in vitro. Recombinant hnRNP-K was incubated in the absence of UCP2 mRNA, with biotinylated UCP2 mRNA or with biotinylated UCP2 mRNA in the presence of a ten-fold excess of non-biotinylated UCP2 mRNA as indicated. Biotinylated mRNA was recovered with immobilized streptavidin and bound hnRNP-K detected by immunoblotting. C, Recombinant hnRNP-K or recombinant hnRNP-K in which tyrosine-458 was changed to phenylalanine (Y458F) was phosphorylated by addition of Src and then tested for binding to biotinylated UCP2 mRNA as above. Blots of bound hnRNP-K as well as input hnRNP-K and tyrosine phosphorylation of input hnRNP-K are shown as indicated. D, Binding of hnRNP-K to UCP2 mRNA was analysed in vitro as above and blots quantified by scanning. Binding is normalized to that in the absence of phosphorylation for each hnRNP-K and presented as means and SEM for three independent experiments (*p < 0.05, Student's ‘t’ test, for the effect of phosphorylation).