Fig 7. Jak1-dependent STAT-activation of the constitutively active gp130ΔYY-mutant depends on CK2.
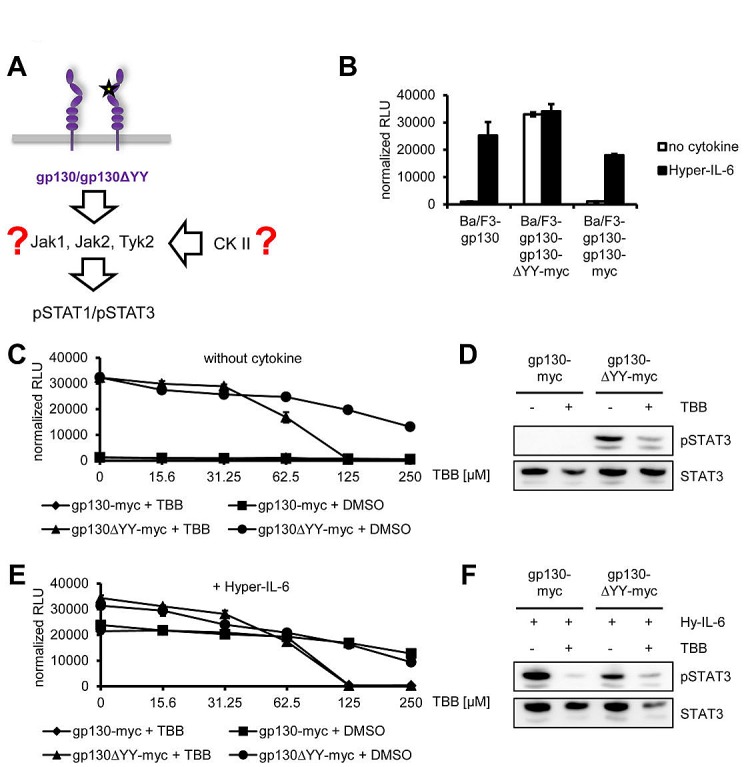
(A) Schematic representation of the gp130ΔYY-mutant harboring a deletion in domain 2. The kinase leading to constitutive STAT activation and the role of CK2 in this are unknown. (B) Equal amounts of Ba/F3-gp130, Ba/F3-gp130-gp130-myc and Ba/F3-gp130-gp130ΔYY-myc cells were incubated with or without 10 ng/ml Hyper-IL-6. (C) Equal amounts of Ba/F3-gp130-gp130-myc and Ba/F3-gp130-gp130ΔYY-myc cells were incubated with either increasing amounts of TBB (0-250 μM) or the corresponding amount of DMSO as control without any cytokine. (D) Equal amounts of Ba/F3-gp130-gp130-myc and Ba/F3-gp130-gp130ΔYY-myc cells were serum-starved for 3 h, and cells were pretreated with 100 μM TBB for 90 min prior to cytokine stimulation where indicated. Phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT3 was assessed by Western blotting, and STAT1/STAT3 served as internal loading control, respectively. (E) Cells were treated as described under panel (B), but 10 ng/ml Hyper-IL-6 was added. (F) Cells were treated as described under panel (D), but cells were stimulated with 10 ng/ml Hyper-IL-6 for 15min. Phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT3 was assessed by Western blotting, and STAT1/STAT3 served as internal loading control, respectively. Cellular proliferation in all assays shown was determined as described in Material and Methods. Proliferation assays as well as Western Blots are one representative experiment of three performed.
