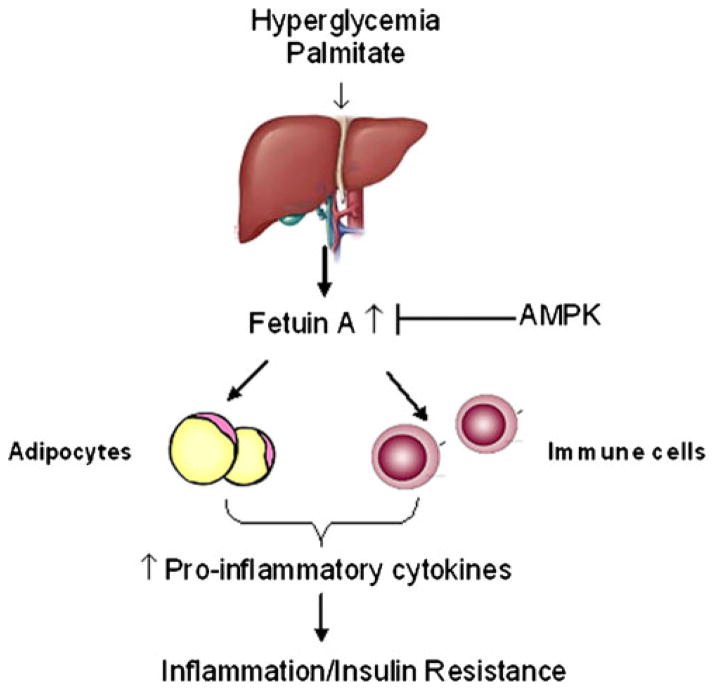
Fig. 2.
Metabolic consequences of fetuin-A production. Hepatic production of the hepatokine fetuin-A can be induced by both increased glucose and palmitate. Fetuin-A is released into the circulation and inhibits insulin signaling by binding to the insulin receptor in insulin-responsive tissues, thereby inhibiting tyrosine autophosphorylation and inducing insulin resistance. Fetuin-A also serves as an adaptor protein for saturated fatty acids, allowing them to activate Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and consequently induce inflammatory signaling and insulin resistance. AMPK can act to 1) suppress fetuin-A production and secretion; 2) diminish fetuin-A induced inflammation; and 3) restore insulin signaling inhibited by fetuin-A