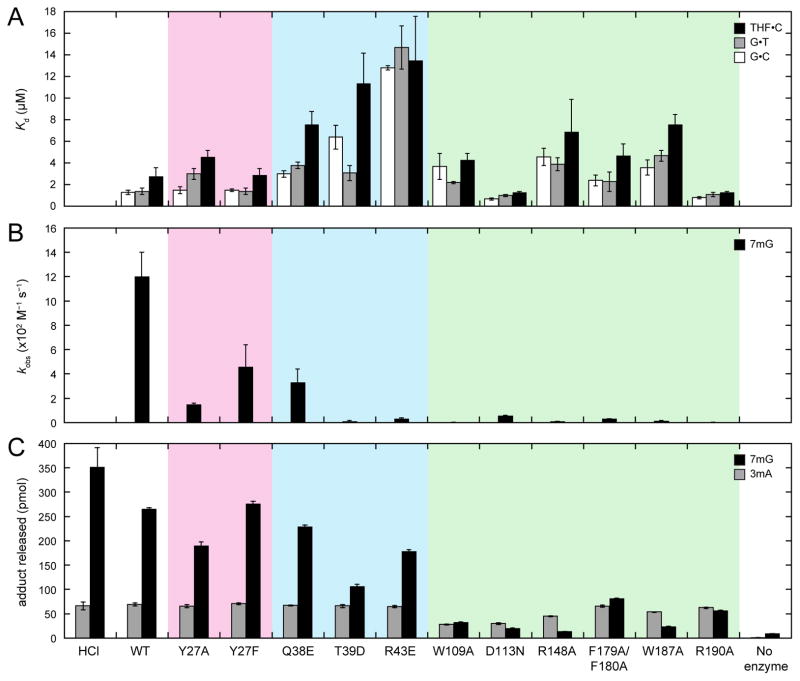
Figure 3. DNA binding affinities and base excision activities of wild-type and mutant AlkD.
(A) Equilibrium dissociation constants (Kd) for binding of FAM-labeled 25-mer oligonucleotide duplexes containing a centrally located G•C (white bars), G•T (gray bars), or THF•C (black bars). (B) Second-order rate constants (kobs) for excision of 7mG (black bars) from a 25-mer oligonucleotide duplex. (C) 3mA (gray bars) and 7mG (black bars) released from methylated genomic DNA. HCl and no-enzyme controls represent the upper and lower limits for adduct removal. All panels show the averages and standard deviations from three experiments. Values are provided in Tables S1–S3. Mutants are colored in accordance with residues in Figure 2.