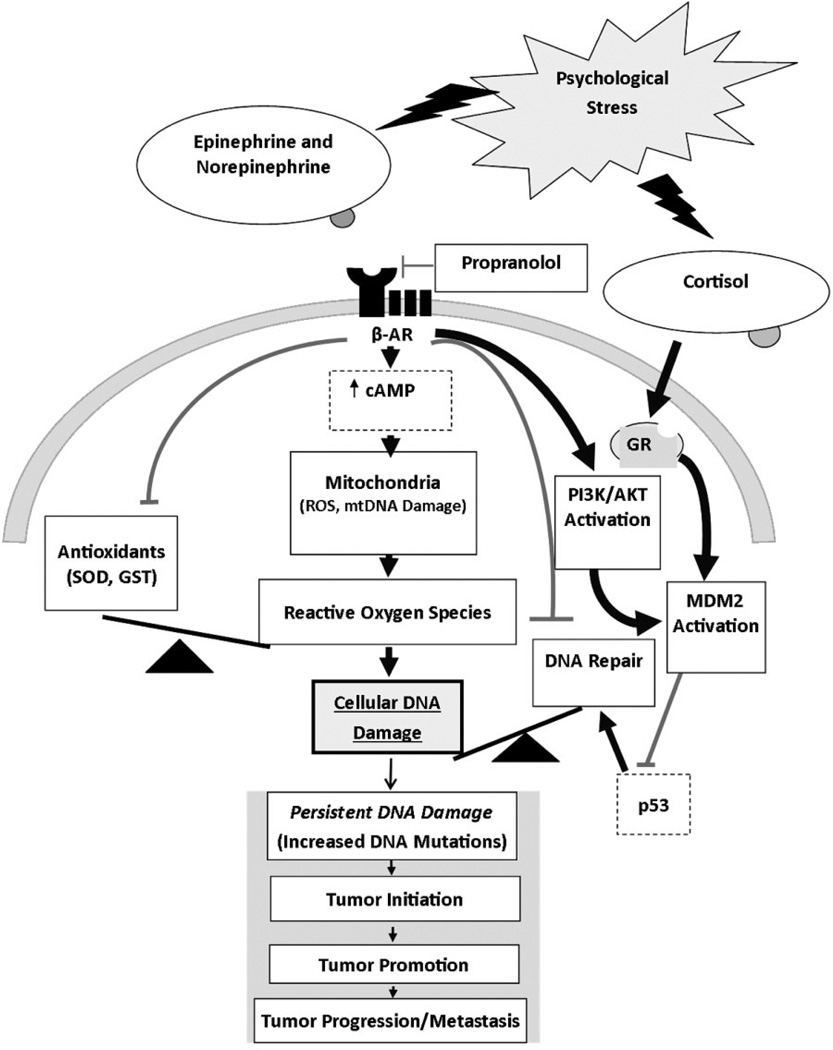
Figure 1.
Empirically based theoretical model of stress-induced effects on DNA damage and/or repair processes as biological mechanisms linking psychological stress to cancer risk. Heavy black lines indicate hypothesized stimulatory effects. Lighter gray lines indicate hypothesized inhibitory effects. β-AR—β-adrenergic receptor; GR—glucocorticoid receptor.