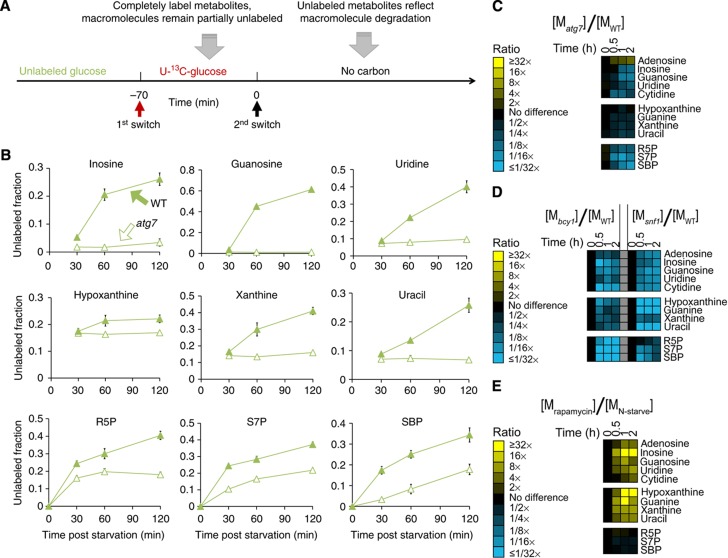
Figure 3.
In carbon starvation, nucleosides and PPP compounds are produced by RNA degradation via autophagy in response to kinase signals. (A) Experimental design for demonstrating metabolite production via macromolecule degradation. Yeast cells were grown on 2% unlabeled glucose, and then switched to U-13C-glucose for 70 min, which completely labels free metabolite but only partially labels macromolecules. Thereafter, glucose was removed and the metabolome analyzed by LC-MS. (B) Fraction of unlabeled nucleosides, nucleic bases and PPP intermediates as a function of starvation time, in wild-type and autophagy deficient (atg7 deletion) yeast. The x axis represents minutes after carbon starvation, and the y axis represents fraction of unlabeled metabolites (mean±range of N=2 biological replicates). (C) Ratio of metabolite levels in atg7 strain versus wild-type strain in carbon starvation. (D) Ratio of metabolite levels in bcy1 strain and snf1 strain versus wild-type strain in carbon starvation. (E) Ratio of metabolite levels in rapamycin treatment versus nitrogen starvation for wild-type yeast. In (C) to (E), all reported values are log2 transformed ratios; data are mean of duplicate samples at each time point.