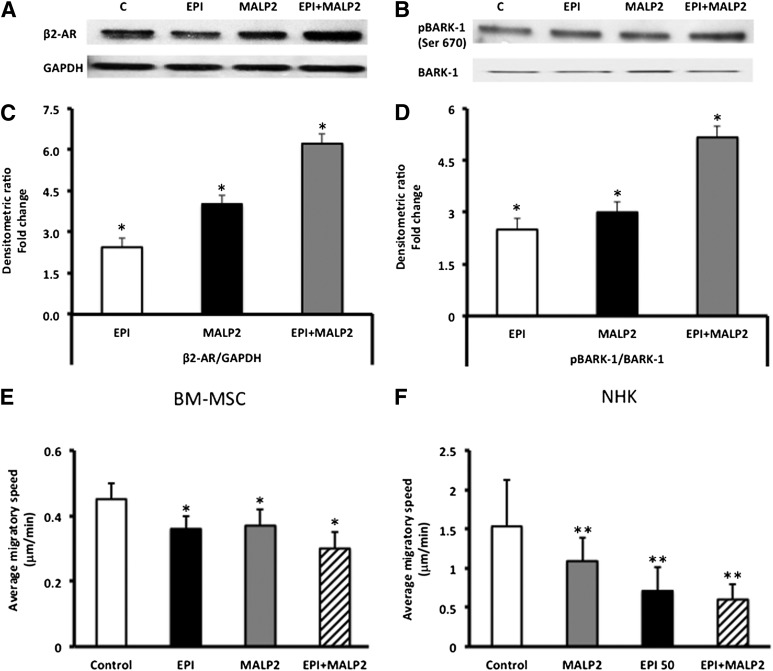
Figure 2.
Synergistic effects of EPI and MALP2 on β2-AR protein expression and BARK-1 phosphorylation in BM-MSCs. (A): Western blot analysis of β2-AR protein expression in EPI (50 nM)-, MALP2 (100 ng/ml)-, and EPI + MALP2-treated cells, as described in Materials and Methods. GAPDH was used as the loading control. (B): Western blot analysis of BARK-1 phosphorylation in EPI (50 nM)-, MALP2 (100 ng/ml)-, and EPI + MALP2-treated cells, as described in Materials and Methods. Total BARK-1 was used as the internal control. (C): Densitometric analysis of the Western blots. β2-AR/GAPDH ratio values are expressed as fold change versus control (mean ± SD). ∗, p < .01 versus control (n = 4). (D): Densitometric analysis of the Western blots. pBARK-1/BARK-1 ratio values are expressed as fold change versus control (mean ± SD). ∗, p < .05 versus control (n = 4). EPI and MALP2 effects on BM-MSC and NHK single-cell migration (SCM). β2-AR and TLR2 activation reduced BM-MSC and NHK migration. (E, F): Migratory speeds of BM-MSCs (E) and NHKs (F) plated on collagen-coated glass-bottomed culture dishes and treated with serum-free growth medium (control), EPI (50 nM), MALP2 (100 ng/ml), or EPI + MALP2 were determined. SCM rates of at least 50 cells per treatment were measured, as described in Materials and Methods. Each panel represents the mean ± SD of at least four experiments (160– 200 cells per treatment) using four cell strains isolated from four different donors. ∗, p < .05 versus BM-MSC control; ∗∗, p < .001 versus NHK control. Abbreviations: β2-ARs, β2-adrenergic receptors; BARK, β-adrenergic receptor-activated kinase; BM-MSCs, bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells; C, control; EPI, epinephrine; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; MALP2, macrophage-activating lipopeptide-2; NHKs, neonatal keratinocytes; pBARK, phospho-BARK.