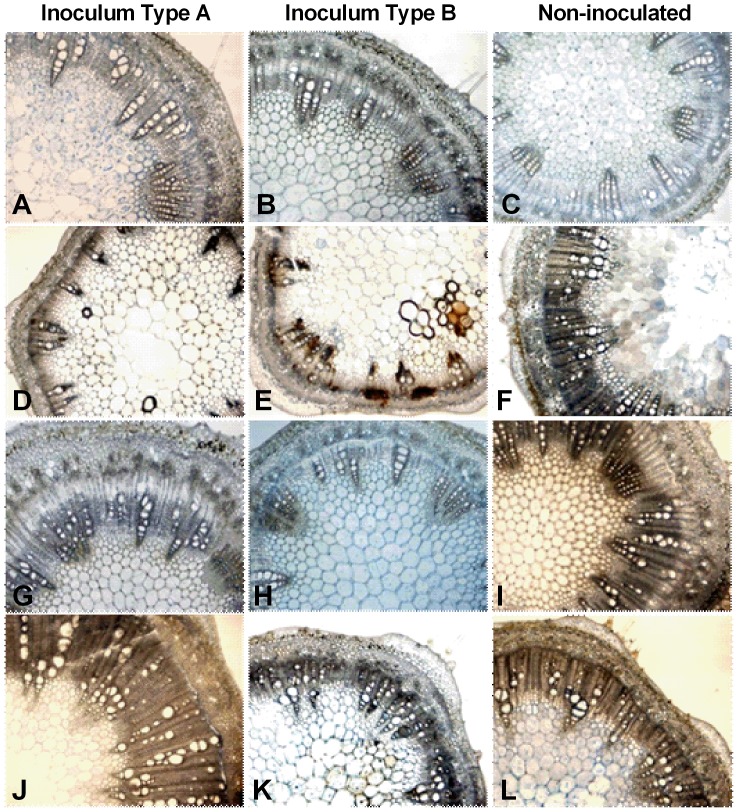
Figure 6. Stem anatomy of soybean during latent and pathogenic infection by Phialophora gregata.
Stem anatomy of the resistant soybean cultivar (Bell) and the susceptible cultivar (Corsoy 79) during latent and pathogenic infection by types A and B of Phialophora gregata. During latent infection (2 weeks post inoculation) no differences were seen in anatomical organization in Corsoy 79 inoculated with type A (A), type B (B) or the control (C), but differences in the vascular cambium and xylem structure was seen during pathogenic infection (6 weeks post inoculation) (D–F). During latent infection of Bell, the vascular organization was similar in plants inoculated with type A (G) and the control (I), but plants infected with type B (H) had less secondary growth and a less pronounced layer of vascular cambium. Differences in anatomical organization were observed during pathogenic infection Bell inoculated with type B (K) had less secondary growth and less of a cambium layer compared to the Bell inoculated with type A (J) and the controls (F, L). All images were taken at 40x magnification. Treatments for experiment 1 were replicated three times (n = 3 plants/replication). Treatments for experiment 3 were replicated three times (n = 4 plants/replication).