Figure 2.
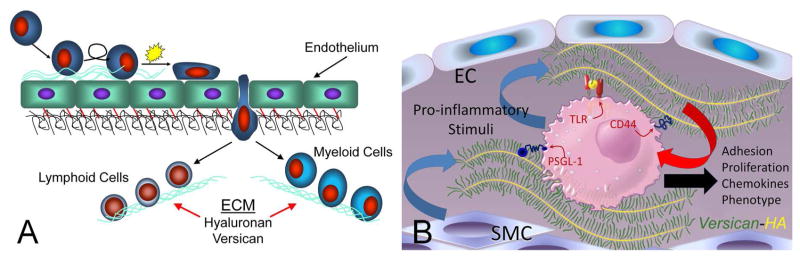
A. Extravasation of myeloid and lymphoid cells across the endothelium into the underlying tissue where they interact with the ECM enriched in versican and HA. (B. ECM and immune cell regulation. Leukocytes come into contact with the ECM as they invade tissue as part of the inflammatory phase of tissue repair. Certain types of ECMs, including those that contain versican and hyaluronan, interact with myeloid and lymphoid cells through specific cell surface receptors such as, PSGL-1, TLR2, and CD44 to promote their adhesion, accumulation, and activation. Such matrices may exhibit either pro- or anti-inflammatory properties. These versican-enriched ECMs may be produced by either stromal cells or the myeloid and lymphoid cells themselves. Image shown in B kindly provided by Dr. Charles W. Frevert, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Panel A is from Wight TN, “The biomatrix of the vascular system and the control of cell phenotype,” Hyaluronan: From Basic Science to Clinical Applications, vol 5, Structure and Function of Biomatrix: Control of Cell Behavior and Gene Expression, Balazs, EA, Editor. Matrix Biology Institute, Edgewater, NJ, 2012, pp. 315–340. Reprinted with permission of the Matrix Biology Institute.
