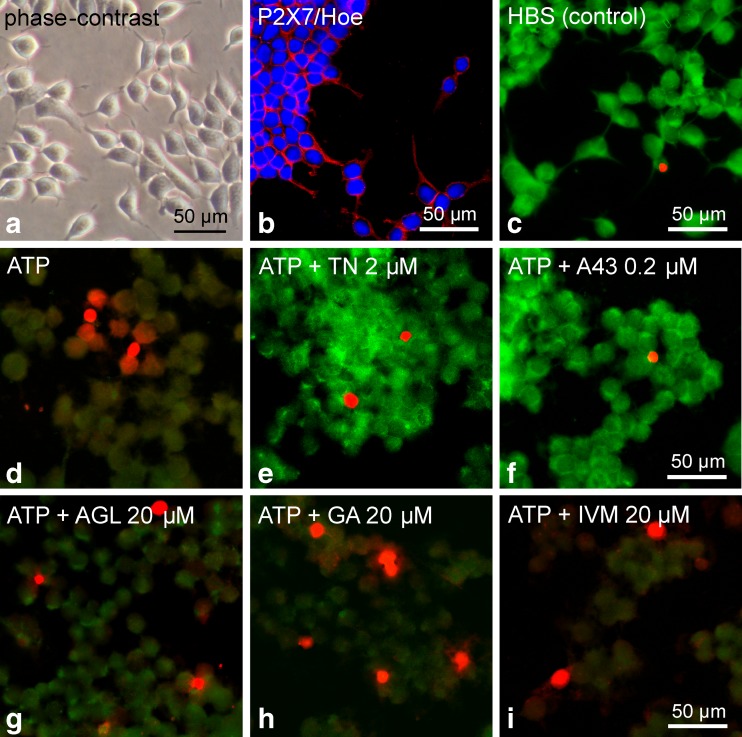
Fig. 12.
Influence of the investigated natural compounds and reference substances on high ATP (2 mM)-induced cell damage in HEK hP2X7 cells. a Representative photomicrograph of a living cell culture. b Confocal image of immunofluorescence demonstrating the expression of P2X7 (Cy3, red) in stably transfected HEK293 cells, additional nucleic acid-staining by Hoechst 33342 (blue). c–i Combined calcein/ethidium staining for discrimination of live, damaged and dead cells. The controls with HBS (c) showed strong green fluorescence as an indicator of living cells that possess esterase activity and intact membranes to retain the esterase products. In contrast, the application of ATP (2 mM, for 20–25 min) induced diminished green calcein fluorescence indicating loss of cell viability, but only a few cells revealed a red nucleic fluorescence of ethidium homodimer-1 representing membrane leakage and dying cells (d). e, f TN (2 μM, pretreatment 10 min before ATP) and the selective P2X7 antagonist A-438079 (A43 0.2 μM, 10 min before ATP) markedly protected the cells (strong green fluorescence). g–i Pretreatment with the positive allosteric modulators AGL, GA and IVM (all 20 μM, 10 min before ATP) revealed damaged cells but did not indicate significantly increased cell death. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Photomicrographs were made by using a confocal laser scanning microscope