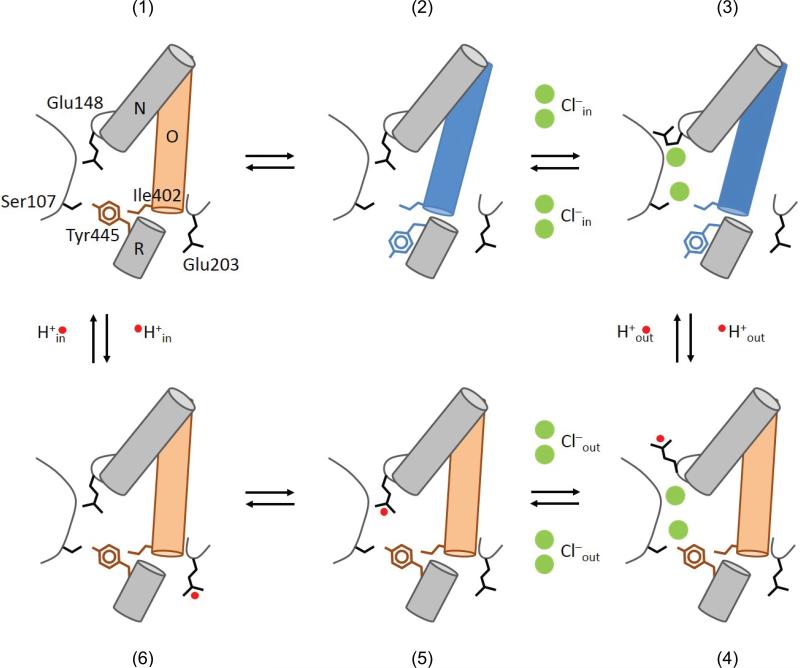
Figure 7. Transport cycle for Cl–H+ exchange in the CLC transporters.
The details of the transport model are given in the main text. The states are (1) Apo state with the inner (Tyr445) and outer (Glu148) gates closed. The inner gate opens (2) thereby allowing Cl– binding to CLC-ec1 (3). (4) The inner gate closes, the external gate opens and becomes protonated. (5) Cl– ions can move to the extracellular solution and the external gate closes while still protonated. (6) The proton goes to the intracellular proton acceptor, Glu203 from which it diffuses into the intracellular solution returning the transporter to the apo state.