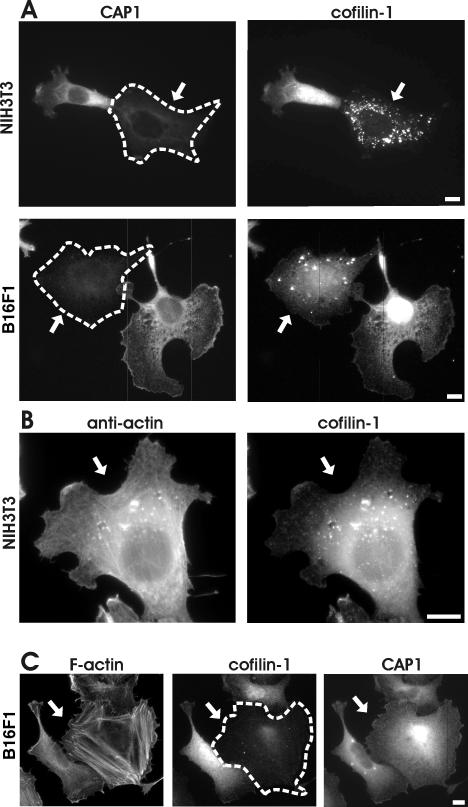
Figure 8.
CAP1 is important for correct subcellular localization and function of cofilin-1. (A) NIH 3T3 (top) and B16F1 (bottom) cells transfected with CAP1 siRNA oligonucleotides were stained with anti-CAP1 (left) and anti-cofilin-1 (right) antibodies. In CAP1 knockdown cells (arrows), cofilin-1 no longer localized to dynamic actin-rich structures, but instead it accumulated to the dot-like structures in the cytoplasm. (B) NIH3T3 cells transfected with CAP1 siRNA were treated with Gdn-HCl to denature proteins and stained with an anti actin (AC-15) (left) and cofilin-1(right) antibodies. The abnormal cofilin aggregates in CAP1 knockdown cells contain also actin. (C) F-actin (left), cofilin-1 (middle), and CAP1 (right) were visualized in B16F1 cells transfected with cofilin-1–specific RNA oligonucleotide duplexes. Cofilin-1 knockdown cell (arrow) shows similar accumulation of actin stress-fibers as seen in CAP1 knockdown cells. However, cofilin-1 depletion does not significantly affect the subcellular localization of CAP1. Bar, 10 μm.