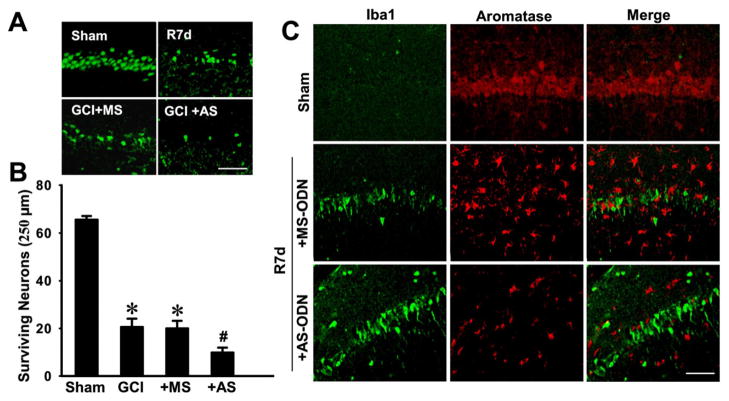
Fig. 5. Antisense oligodeoxynucleotide (AS-ODN) knockdown of aromatase and brain-derived E2 levels in the hippocampal CA1 region of ovariectomized rats leads to enhanced neuronal damage and microglia activation following global cerebral ischemia (GCI).
(A) Typical staining with NeuN of hippocampal sections from sham, GCI reperfusion 7 days (R7d), or GCI reperfusion 7 days aromatase AS-ODN or MS-ODN groups. (B) Quantitative analyses of the number of surviving neurons per 250μm length of medial CA1. NeuN-positive CA1 pyramidal cells showing intact and round nuclei were counted as surviving cells. Data are means±SE. *P<0.05 vs. sham, #P<0.05 vs. MS group. N = 5 per group. (C) Typical confocal microscopy images showing the double staining of iba1 and aromatase in hippocampal CA1 region from sham and GCI post reperfusion 7 days rats pretreated with aromatase AS-ODN or MS-ODN. Note that aromatase knockdown in ovariectomized rats leads to enhanced microglia activation, and that aromatase was not expressed in activated microglial cells. Scale bar, 50 μm. Magnification, 40×.