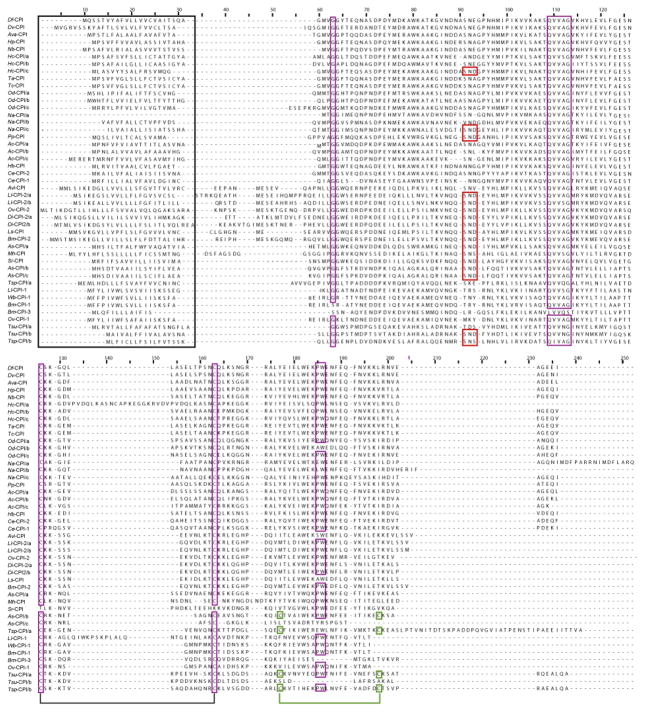
Fig. 2.
Sequence comparison. Alignment of amino acid sequences of type 2-like cystatins predicted for Dictyocaulus filaria (Df) and Dictyocaulus viviparus (Dv) with those of 24 other species of nematodes (see Table 3) and key structural and functional elements in these sequences. Key elements identified based on the tertiary structure of cystatin from chicken egg white (Bode et al., 1988) are: the signal peptide (outlined in black); residues involved in C1 papain-like peptidase binding (purple) including the N-terminus glycine (position 63; labeled as G in Table 3); the inhibitor domain for C1 papain-like peptidase (positions 113–117; QXVXG); the first, central cysteine disulfide bond (positions 131 and 159); and the C-terminus domain (positions 181 and 182; PW); the second C-terminus cysteine disulfide bond (positions 173 and 194; green); and the motif involved in the binding of the mammalian asparaginyl endopeptidase (SND/SNS; positions 95–97; red). Ac, Ancylostoma caninum; As, Ascaris suum; Ava, Angiostrongylus vasorum; Avi, Acanthocheilonema viteae; Bm, Brugia malayi; Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans; Di, Dirofilaria immitis; Hb, Heterorhabditis bacteriophora; Hc, Haemonchus contortus; Hp, Heligmosomoides polygyrus; Ll, Loa loa; Ls, Litomosoides sigmodontis; Mh, Meloidogyne hapla; Na, Necator americanus; Nb, Nippostrongylus brasiliensis; Od, Oesophagostomum dentatum; Ov, Onchocerca volvulus; Pp, Pristionchus pacificus; Sr, Strongyloides ratti; Ta, Trichostrongylus axei; Tc, Trichostrongylus colubriformis; Tsp, Trichinella spiralis; Tsu, Trichuris suis; Wb, Wuchereria bancrofti.