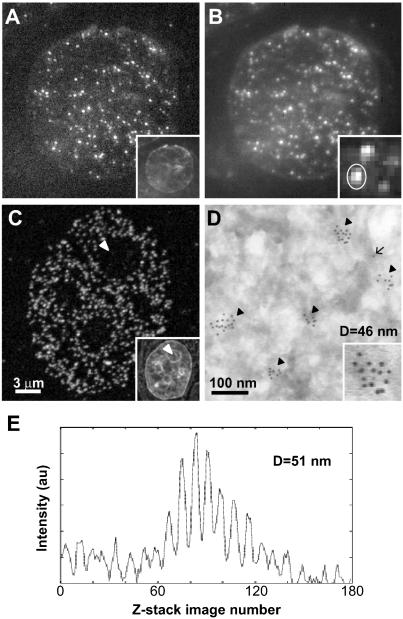
Figure 2.
Measuring the size of pol IIO discrete sites. Pol IIO occur as sites throughout the nucleoplasm in sites SMI-microscopy (A and B), CLSM (C), and EM (D) images. HeLa cells were fixed, embedded in sucrose, and cryosectioned (∼140 nm in thickness). Pol IIO was indirectly immunolabeled using mAb H5 and Alexa Fluor 488 (A–C) or 5-nm gold particles (D); sections were counter-stained with TOTO-3 (insets in A and C) or uranyl acetate (D), and images were collected with an SMI-microscope (A and B), CLSM (C), or EM (D). (A) An x,y image from the center of a z-stack of 160 images collected with the SMI-microscope. Due to the modulation of the incident light (see text), some sites cannot be seen in this image. (B) In a projected image of the 160 z-stack images, all sites detected by SMI-microscopy can be seen. The inset shows an enlarged view of several sites. (C) CLSM detects a greater number of sites, which are absent from nucleoli (arrowhead; see text). (D) On the EM, sites occur as clusters (arrowheads) of gold particles, and lone particles (arrow) represent nonspecific background; the inset shows an enlarged view of one cluster. EM detects the highest number of sites due to increased resolution. (E) Emission profile produced by the site circled in B (inset) giving a diameter of 51 nm.