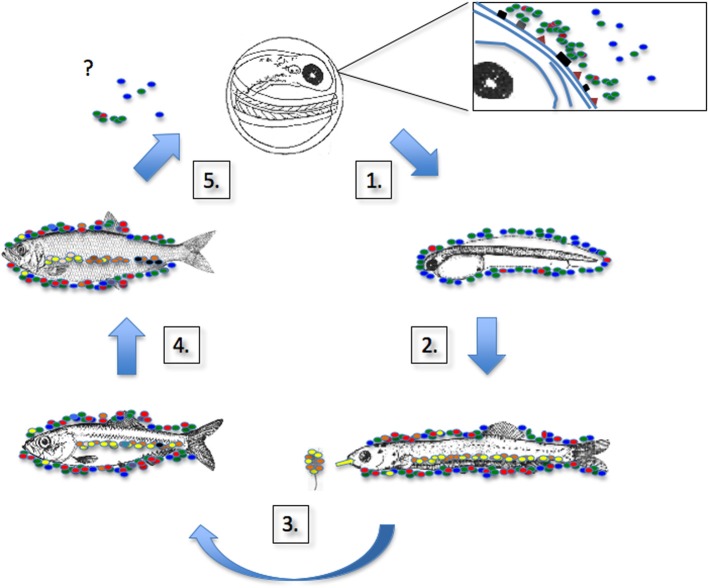
Figure 3.
Teleost microbiome during development. Figure shows schematic of the generalized lifecycle of a teleost and accessory indigenous bacteria (different taxa represented by colored elipses). (1) Bacteria colonize the chorion of the egg. Taxonomic differences of bacteria between fish species suggest specific early interactions, perhaps through precursors of innate immunity (symbolized by squares and triangles on the chorion surface). (2) Egg hatches, larval is colonized by environmental bacteria as well as those originally present on the chorion. (3) Early digestive tract colonization occurs when larva commence feeding. Bacterial taxa strongly resemble those associated with food source. (4) Microbiome develops, accumulates diversity and matures. (5) Adult microbiome is diverse assemblage of microbial taxa. Differences exist between surface mucosal and intestinal communities. Intestinal communities also be compartmentalized/specialized to niches within the alimentary tract. Question mark indicates possible vertical transmission of microbiome components to eggs during oviposition.