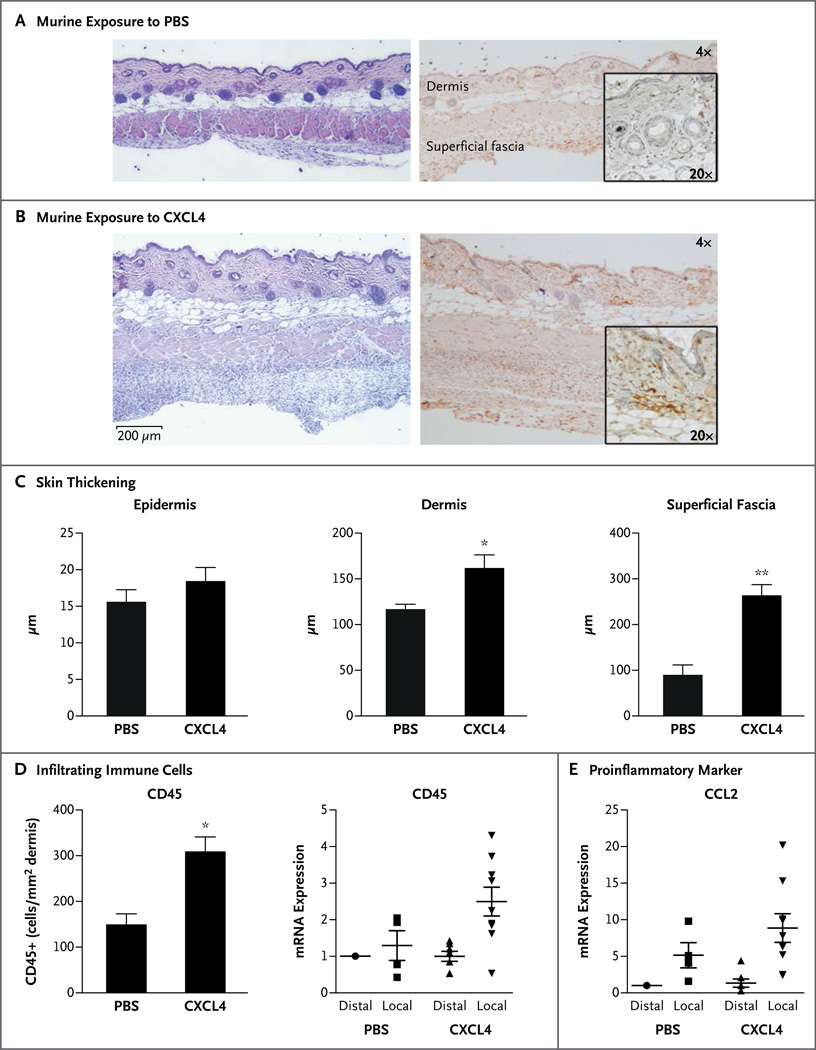
Figure 4. (facing page). Inflammatory Skin Changes Mimicking Those in Systemic Sclerosis Induced by CXCL4 In Vivo in Mice.
Panels A and B show the results of histologic analyses of skin from wild-type C57BL/6 mice that were treated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) as a control (Panel A) or with CXCL4 (Panel B) for 7 days with the use of a subcutaneous-pump model, shown at 4× and 20× magnification (hematoxylin and eosin, left; CD45 immunohistochemical staining, right). The murine sample that was treated with CXCL4 shows marked infiltration of inflammatory cells in the dermis and subdermis, as compared with the control sample. Panel C shows quantification of the thickening of skin layers after CXCL4 treatment for 7 days with the use of the pump model, as compared with the PBS controls. Shown are mean values for three analyses in each group, with T bars indicating standard errors. Panel D shows the quantification of infiltrating immune cells after 7-day exposure to CXCL4 or PBS, in which CD45+ cells in the dermis were counted after immunohistochemical staining; the means of three analyses per group are shown (at left). In addition, the influx of inflammatory cells is confirmed by increased CD45 messenger RNA (mRNA) expression in CXCL4-exposed skin isolated from the distal or proximal (local) area to the pump outlet, as measured on quantitative polymerasechain-reaction (PCR) assay (at right). In Panels C and D, a single asterisk denotes P<0.05 for the between-group comparison; double asterisks denote P<0.01. Panel E shows the mRNA expression of proinflammatory marker CCL2 induced after 7-day exposure to CXCL4, as compared with PBS, also measured on quantitative PCR assay. In Panels D and E, the mRNA analyses included 4 samples for PBS and 7 samples for CXCL4. The horizontal lines indicate means, and I bars standard errors.