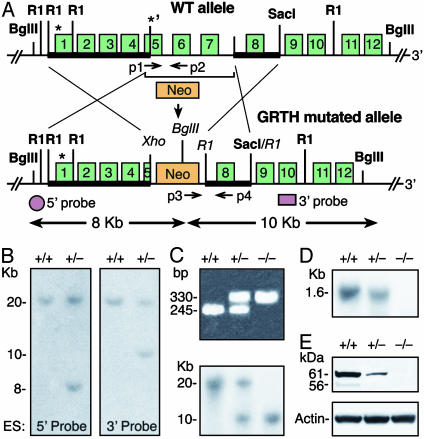
Fig. 2.
Targeted disruption of the GRTH gene. (A) Targeted gene construction. (Upper) Wild-type mouse GRTH gene allele. *, ATGs. Bold line indicates the homologous 5′ arm (exons 1–4 and part of exon 5) and the 3′ arm (2.9-kb fragment with exon 8, 5′ and 3′ intron sequences) were subcloned at NotI/Xho and R1 site, respectively, in the targeting vector pPNT with (Neo) and (TK) selection markers. (Lower) The GRTH mutated homologus recombinant allele. Shown are the 5′ and 3′ probes used for Southern analysis and the PCR primers used for genotype screening (p1-p4). (B) Screening ES clones by Southern analysis. Positive homologous recombinant clones were identified with BglII digestion (predicted size: wild-type, 20 kb; recombinant allele with 5′ probe, 8 kb, and 3′ probe, 10 kb). (C) Genotyping of offspring mice by PCR (Upper). Predicted size: GRTH+/+, 245 bp (p1/p2); GRTH+/-, 245 bp (p1/p2) and 330 bp (p3/p4); and GRTH-/- mice, 330 bp (p3/p4). Positive clones were confirmed by Southern analysis by using a 3′ probe (Lower). (D and E) Northern (D) and Western (E) analyses of testis from adult GRTH+/+, GRTH+/-, and GRTH-/- mice.