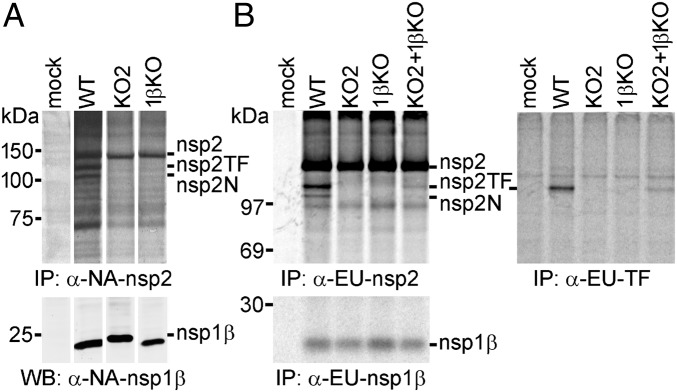
Fig. 6.
A conserved motif in PRRSV PLP1β is critical for transactivation of −2/−1 PRF in infected cells. (A) Analysis of nsp2-related products in MARC-145 cells infected with WT type 2 PRRSV (isolate SD95-21) or mutants KO2 and 1βKO. Mutant KO2 (Fig. S1) contained PRF-inactivating point mutations in both slippery sequence and downstream C-rich motif, whereas 1βKO carried a double Ala substitution of basic residues in the highly conserved GKYLQRRLQ motif of nsp1β. Following metabolic labeling, proteins were immunoprecipitated using mAb α-NA-nsp2 and visualized by SDS/PAGE and autoradiography. The expression of nsp1β was monitored by Western blot analysis. Samples in all rows were run on the same gel, but gel/blot images were spliced to remove lanes derived from samples not related to this study and to achieve a lane order consistent with B. (B) BHK-21 cells were transfected with in vitro-transcribed full-length RNA of WT, KO2, or 1βKO PRRSV SD01-08 (type 1) or were double transfected with equal amounts of KO2 and 1βKO RNA to demonstrate complementation between these two virus mutants. Following metabolic labeling, viral proteins were immunoprecipitated using specific mAbs that recognize a common nsp2 domain (Upper Left), the polypeptide encoded by the TF ORF (Upper Right), or nsp1β (Lower). Protein products were visualized using SDS/PAGE and autoradiography.