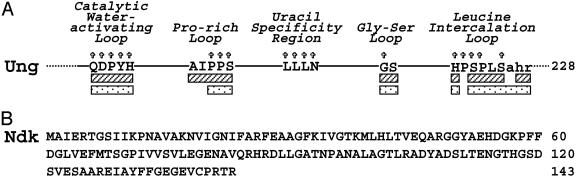
Fig. 1.
Conserved motifs of E. coli Ung and amino acid sequence of E. coli Ndk. (A) Five structural motifs, previously implicated by Putnam et al. (18) as critical to Ung activity, are illustrated. Capitalized amino acids indicate structurally equivalent residues in E. coli, human, and herpes simplex virus uracil-DNA glycosylases as determined by high-resolution crystal structures (18, 34, 35). Starred residues correspond to amino acids that are absolutely conserved in E. coli, human, herpes simplex virus, and B. subtilis uracil-DNA glycosylase polypeptides. Striped and speckled bars correspond to residues that contact Ugi and DNA containing an AP-site, respectively. (B) The amino acid sequence of E. coli Ndk, as described by Hama et al. (2), is shown.