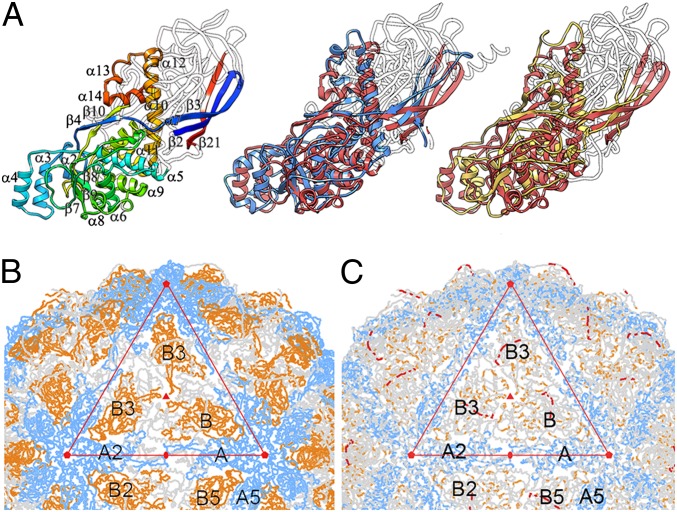
Fig. 5.
Structural homology of the PcV fold with L-A virus Gag CP. (A) Gag structure, rainbow-colored, indicating each conserved SSE relative to the PcV basic CP domain (Left) and structural alignments of domains A (blue, Center) and B (yellow, Right) with Gag (red). White segments are nonsuperimposed regions (the 36-residue N-terminal segment of domain A is omitted). (B) PcV capsid showing A (blue) and B (yellow) domain segments structurally aligned with Gag A and B monomers (variable regions, gray). Interactions at the fivefold axis (pentagons) are fully conserved, as are those at the twofold (oval) and threefold (solid triangle) axes. The large triangle defines an icosahedral face. A and B domains (or monomers for L-A) are related to neighboring domains by icosahedral symmetry (A to A5 by fivefold rotation). (C) PcV capsid showing A (blue) and B (yellow) domain segments and the linker (red) conserved among several chrysovirus CP sequences (variable regions, gray).