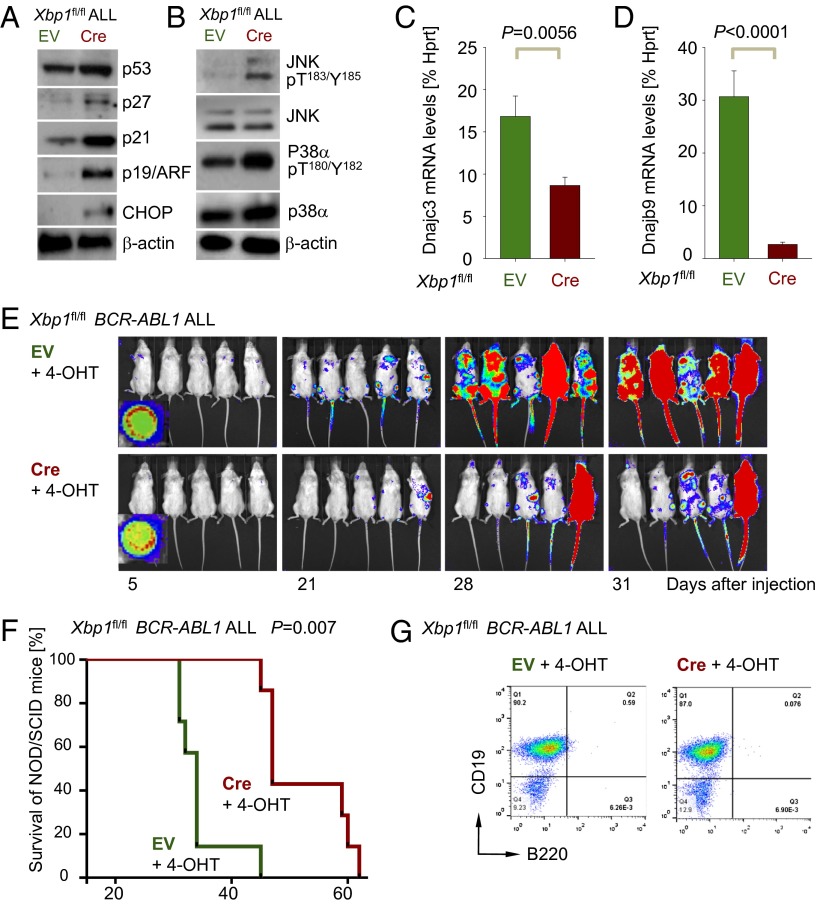
Fig. 4.
Loss of Xbp1 function activates proapoptotic pathways and prolongs survival of BCR-ABL1 pre-B ALL transplant recipient mice. (A) Protein levels of Arf (Cdkn2a), p53, p21 (Cdkn1a), p27 (Cdkn1b), and Chop were studied by Western blot analysis in Xbp1fl/fl ALL cells with (Cre) or without (EV) deletion of Xbp1 using β-actin as loading control (n = 3). (B) Likewise, phosphorylation of MAP kinases p38α (T180/Y182) and JNK1/2 (T183/Y185) were assessed (n = 3). (C and D) mRNA levels of DnajC3 (p58IPK) and DnajB9 (Erdj4) were measured in Xbp1fl/fl ALL cells with (Cre) or without (EV) deletion of Xbp1 by qRT-PCR (n = 3). (E) One million luciferase-labeled Xbp1fl/fl ALL cells with EV or Cre were injected (i.v.) into sublethally irradiated (2.5 Gy) NOD/SCID mice and leukemic expansion was tracked by luciferase bioimaging. (F) Overall survival of transplant recipient mice is shown in a Kaplan–Meier analysis (n = 7 per group). (G) A representative FACS analysis for surface markers CD19 and B220 (n = 4) is shown for Xbp1fl/fl ALL cells isolated from killed mice.