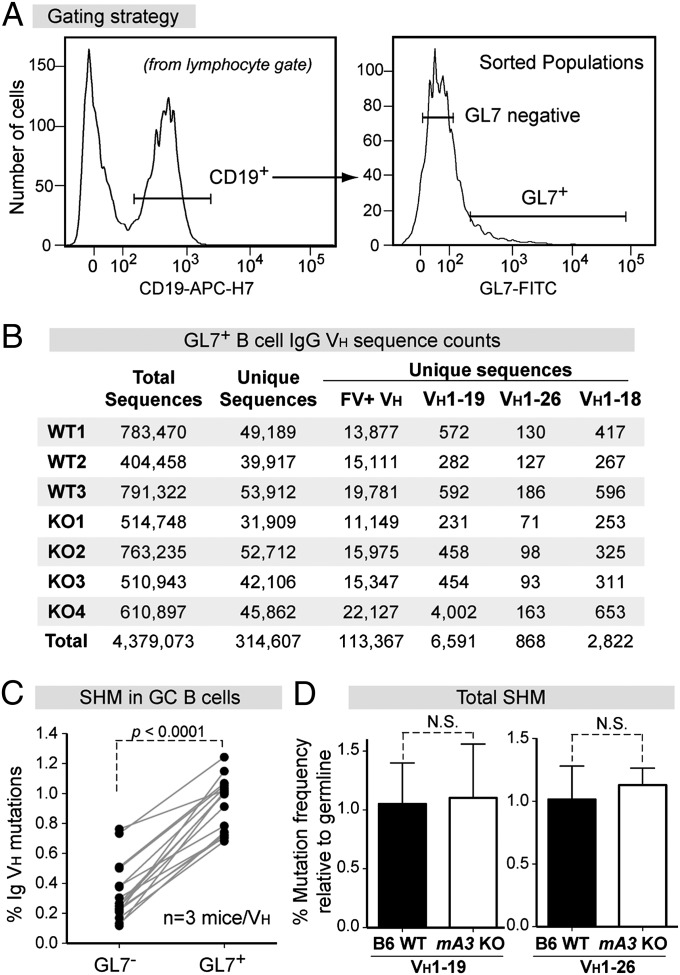
Fig. 2.
NGS of GC B-cell VH genes from B6 WT versus mA3 KO mice. (A) Sorting strategy. RNA extracted from CD19+GL7+ cells were used for cDNA synthesis followed by IgG VH PCR with Illumina primers. (B) Sequence read counts from individual WT and KO mice. To minimize selection bias, identical sequences were collapsed into a single unique sequence. FV+ VH corresponds to the 16 VH genes in the FV-specific mAbs in Fig. 1G. (C) Validation of sorted GC B cells. The average mutation frequencies of paired GL7+ and GL7− populations from the three WT mice were computed for each of the 16 VH genes. Differences were evaluated using a two-tailed paired Student t test. (D) Total mutation frequency in WT (n = 3) and KO (n = 4) mice for VH1–19 and VH1–26 sequences. Differences were evaluated using a two-tailed unpaired Student t test with P < 0.05 considered as significant.