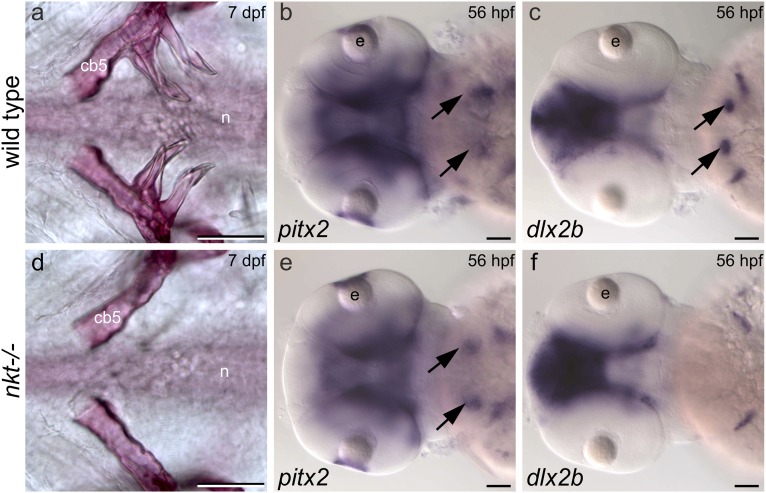
Fig. 2.
The nkt mutation in eda results in early arrest of pharyngeal tooth development. (A and D) Ventral views of alizarin stained 7-dpf larvae showing complete absence of teeth in an nkt mutant homozygote. A single tooth is sometimes formed on one side of these mutants (n = 4 of 19). (B and E) pitx2 is expressed in presumptive pharyngeal tooth epithelium (arrows) in the nkt mutant homozygote (n = 5 of 5), heterozygote (n = 11 of 11), and wild-type homozygote (n = 5 of 5). (C and F) dlx2b is expressed in pharyngeal tooth germs (arrows) of wild-type homozygotes (n = 3 of 3) and nkt heterozygotes (n = 12 of 12), but its expression is lacking in the pharynx of the nkt mutant homozygote (n = 5 of 5). Abbreviations: cb5, fifth ceratobranchial bone; e, eye; hpf, hours postfertilization; n, notochord. (Scale bars, 50 μm.)