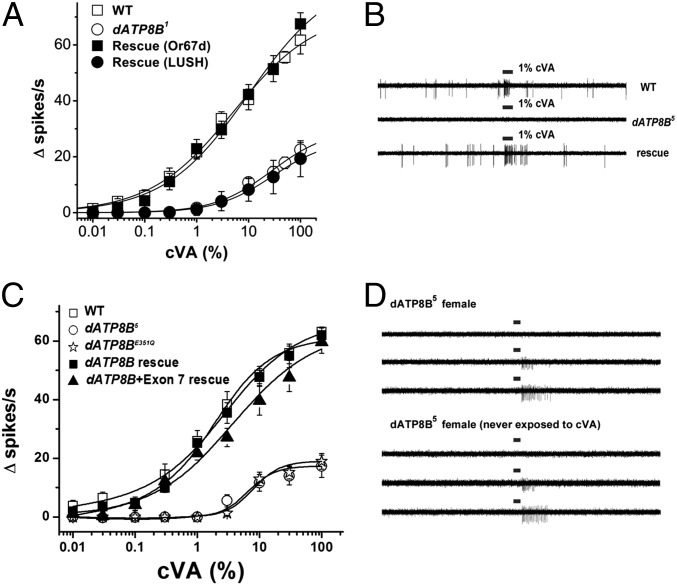
Fig. 3.
dATP8B is required for normal function in Or67d neurons. (A) dATP8B1 homozygous mutants (open circles) have defective cVA responses compared with wild-type controls (open squares). Expression of a dATP8B cDNA regulated by the Or67d promoter (rescue Or67d, genotype w ; UAS Or67d /+ ; Or67dGAL4, dATP8B1/dATP8B1) restores dATP8B1 mutants to wild-type cVA sensitivity (closed squares), but expression of dATP8B in support cells of dATP8B1 mutants using the lush promoter (rescue LUSH, closed circles; genotype w ; UAS dATP8B/LUSH GAL4 ; dATP8B1) fails to rescue cVA sensitivity. (B) Sample traces showing rescue of normal spontaneous activity and 1% cVA sensitivity to Or67d neurons from dATP8B5 mutants by expressing a dATP8B cDNA with a single copy of Or67dGAL4. (C) cVA dose–response curves for wild-type (open boxes), dATP8B5 mutants (open circles), and transgenic flies expressing wild-type (filled boxes) or dATP8BE351Q mutant dATP8B cDNAs (open stars) in the dATP8B5 mutant background. A longer dATP8B cDNA, including exon 7 also rescues (filled triangles). n = 6–8. (D) dATP8B5 mutants never exposed to cVA show typical defects. (Upper) Responses of dATP8B5 females raised in mixed cultures to 300-ms pulses of air with 1%, 10%, or 100% cVA. (Lower) Female dATP8B5 mutants isolated as larvae, raised in isolation, and never exposed to cVA before testing are not different from those raised in mixed culture.