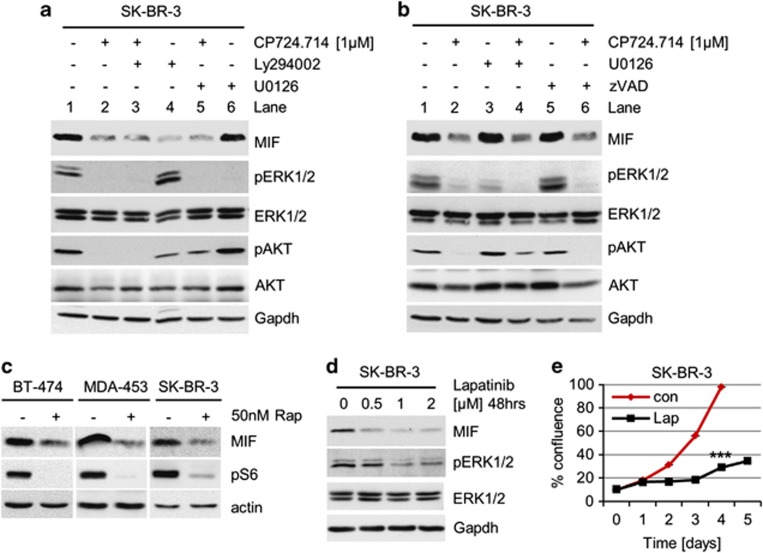
Figure 2.
Blocking the HER2–PI3K–mTOR pathway reduces MIF protein levels. (a and b) Inhibition of the HER2–PI3K axis, but not the HER2–MEK–ERK1/2 axis, destabilizes MIF protein. SK-BR-3 cells were treated with 1 μM CP724.714 (specific HER2 inhibitor), 25 μM Ly294002 (PI3K inhibitor) or 10 μM U0126 (MEK1/2 inhibitor) (a), or with 1 μM CP724.714, 10 μM U0126 or 50 μM zVAD (panCaspase inhibitor) (b) alone or in combination as indicated. Immunoblot analyses. pERK1/2 and pAKT staining serve as positive control for respective inhibition. Gapdh, loading control. (c) Inhibition of mTOR destabilizes MIF protein. HER2-overexpressing BT-474, MDA-MB-453 and SK-BR-3 cells were treated with 50 nM of Rapamycin for 48 h or left untreated. Immunoblot analyses. pS6 serves as functional control of mTOR inhibition. Actin, loading control. (d) The dual HER2/EGFR inhibitor Lapatinib markedly reduces MIF levels. SK-BR-3 cells were treated or not with Lapatinib for 48 h. Immunoblot analysis. pERK1/2 is a functional control for HER2 inhibition. Gapdh, loading control. (e) Lapatinib blocks survival. SK-BR-3 cells were seeded (day 0) and cultured for 24 h (day 1). Cells were then treated or left untreated with 2 μM Lapatinib for 48 h and followed up to day 5. Confluence measured daily by CELIGO Cytometer. Error bars indicate the S.E.M. of a triplicate experiment. Student's t-test of day 4, two-tailed, P-value: ***P<0.001