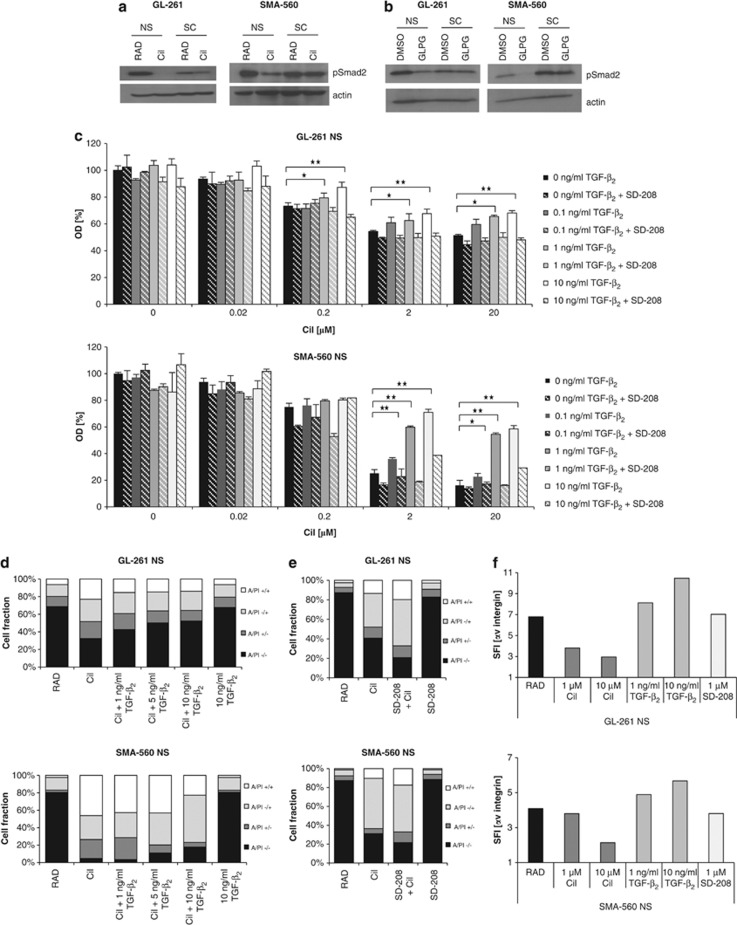
Figure 7.
TGF-β2 counteracts integrin inhibition-induced cell death. (a) GL-261 (left) or SMA-560 (right) NS cells or SCs were exposed to RAD or cilengitide (10 μM). (b) GL-261 (left) or SMA-560 (right) NS cells or SCs were exposed to DMSO or GLPG0187 (1 nM). Subsequently, whole-cell protein lysates were assessed for pSmad2 levels by immunoblot, using actin as a loading control. (c) GL-261 NS cells or SMA-560 NS cells were exposed to combinations of cilengitide and TGF-β2 as indicated with or without SD-208 (1 μM). Metabolic activity was assessed using MTT assay. (d) GL-261 NS cells or SMA-560 NS cells were exposed to RAD, cilengitide (10 μM), TGF-β2 (10 ng/ml) or a combination of cilengitide (10 μM) and increasing concentrations of TGF-β2 as indicated for 48 h. Viability was assessed by annexin V/PI staining. (e) GL-261 NS cells or SMA-560 NS cells were exposed to RAD, cilengitide (10 μM), SD-208 (1 μM) or a combination of cilengitide (10 μM) and SD-208 (1 μM) for 48 h. Cell viability was assessed by annexin V/PI staining. (f) The αv protein levels were assessed by flow cytometry in GL-261 NS cells or SMA-560 NS cells exposed to RAD (10 μM), cilengitide (1 or 10 μM), TGF-β2 (1 or 10 ng/ml) or SD-208 (1 μM) for 48 h