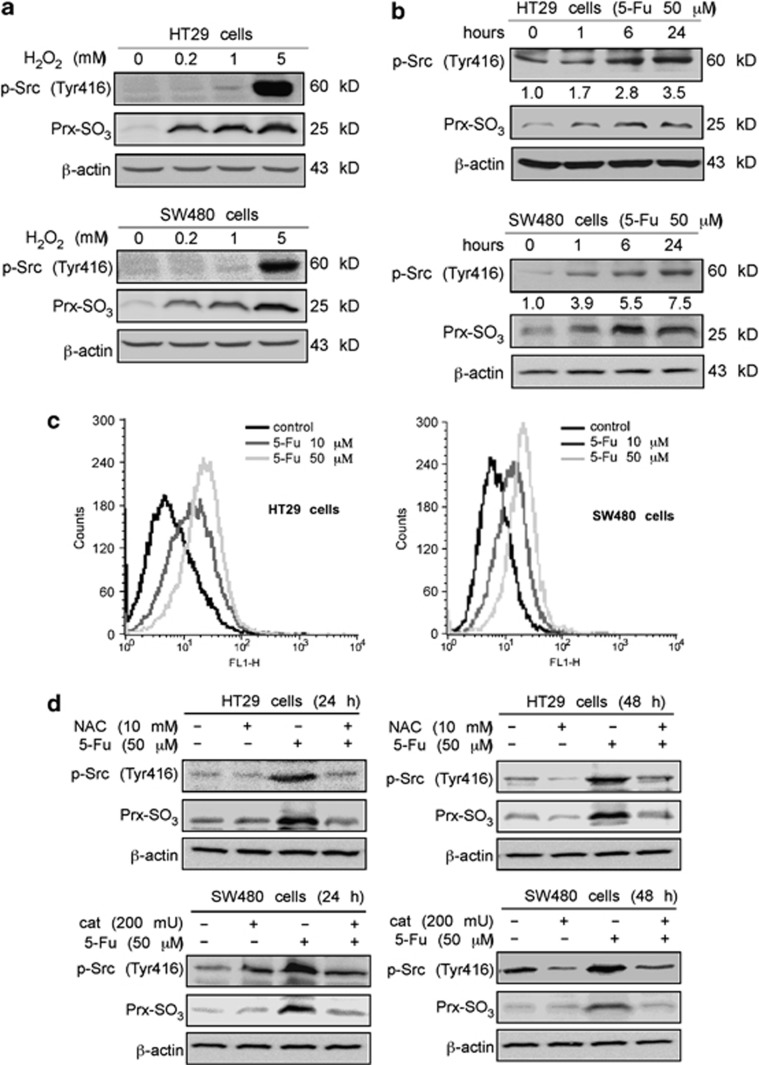
Figure 2.
5-Fu-induced Src activation is mediated by reactive oxygen species (ROS). (a) ROS induce Src activation in colon cancer cells. After treatment with various doses of H2O2 for 30 min, cells were harvested. Phosphorylation of Src (Tyr416) and total Prx-SO3 in whole-cell lysates were detected by western blot analysis. (b) Effect of 5-Fu on Src activation and ROS generation. HT29 and SW480 colon cancer cells were treated with 5-Fu (50 μM) for various times. Phosphorylated Src (Tyr416) and total Prx-SO3 levels were determined by western blot analysis. Fold changes in Src activity after 5-Fu treatment are labeled below the western blot image and were calculated using the Image J (NIH) software program. (c) Generation of ROS with increasing concentrations of 5-Fu. HT29 and SW480 cells were treated for 48 h with 5-Fu at the dose indicated. Cells were then incubated for 30 min at 37 °C with 2.5 μM CellROX Green Reagent. FACS Calibur flow cytometry was used to detect ROS as described in Materials and Methods. (d) Effect of combining NAC or catalase and 5-Fu on Src activation. HT29 and SW480 colon cancer cells were pretreated with NAC (10 mM) or catalase (200 mU) for 2 h and then incubated for 24 or 48 h with 5-Fu (50 μM). Phosphorylated Src (Tyr416) and total Prx-SO3 levels were determined by western blotting. β-Actin was detected in the same membrane and served as a loading control. Data shown are representative of results from triplicate independent experiments