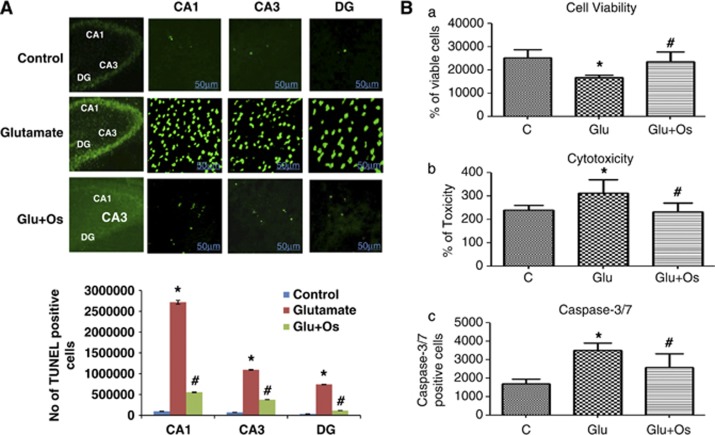
Figure 3.
The effect of osmotin on glutamate-induced DNA fragmentation in the hippocampus of the developing brain. (A) The effect of treatment with osmotin on glutamate-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration. Representative photomicrographs of TUNEL staining are shown that reveal apoptotic neuronal cells after glutamate and osmotin treatment. TUNEL-stained apoptotic neurons are shown in the CA1, CA3 and DG regions of the hippocampus. The change in TUNEL-positive cells indicates that osmotin effectively reduced glutamate-induced apoptosis in these three regions of the hippocampus. Images are representative of the staining observed in each section (n=5 animals/group). TUNEL-stained brain tissue at a low magnification ( × 10) and higher magnification ( × 400). TUNEL-positive cells in the different regions of each section were counted using a computer-based program. Significant differences were determined using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Student's t-test. *Significantly different from the control (CA1, CA3, DG); #significantly different from glutamate (CA1, CA3, DG); significance=P<0.05. (B) Histogram showing (a) cell viability, (b) cytotoxicity and (c) caspase-3/7 assays performed using the ApoTox-Glo Triplex Assay (Promega, Promega BioSciences, LLC., San Luis Obispo, CA, USA). All the related experimental details are provided in the Materials and Methods section. *Significantly different from the control; #significantly different from glutamate; significance=P<0.05