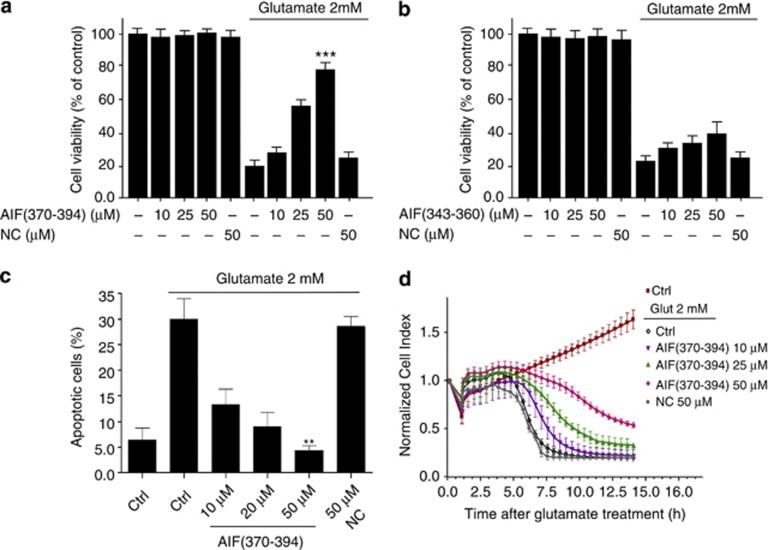
Figure 4.
AIF(370–394) delivery abrogates glutamate-mediated cell death. (a and b) HT-22 cells were transfected with three doses of AIF(370–394) or AIF(343–360) peptides (10 μM, 25 μM, 50 μM) or with an unrelated peptide (NC), used as negative control, at the highest concentration tested (50 μM). Cell viability after glutamate treatment (2 mM for 12 h) was assessed by the MTT assay. As shown, only the presence of AIF(370–394), which binds to CypA, protected cells from the glutamate-induced death in a concentration-dependent manner. Results are presented as percentage of controls considered to be 100% and represent the mean±S.D. of at least four independent experiments performed in quadruplicate. (c) To confirm that apoptosis occurred in glutamate-treated cells and that peptide protection influenced this process, peptide-transfected HT-22 cells were treated with 2 mM glutamate (12 h) or untreated (control) and labeled with Annexin-V-FITC/PI. Finally, they were analyzed by flow cytometry. As shown, the number of apoptotic cells was strongly diminished in the presence of increasing concentrations of AIF(370–394). Percentages reported in the bar graph refer to double-positive stained cells (n=4). (d) HT-22 cells were treated with 2 mM glutamate after transfection with AIF(370–394) or with an unrelated peptide used as negative control (NC). Data show that up to 15 h from the initial glutamate-induced damage, AIF(370–394) afforded protection in a time- and dose-dependent way