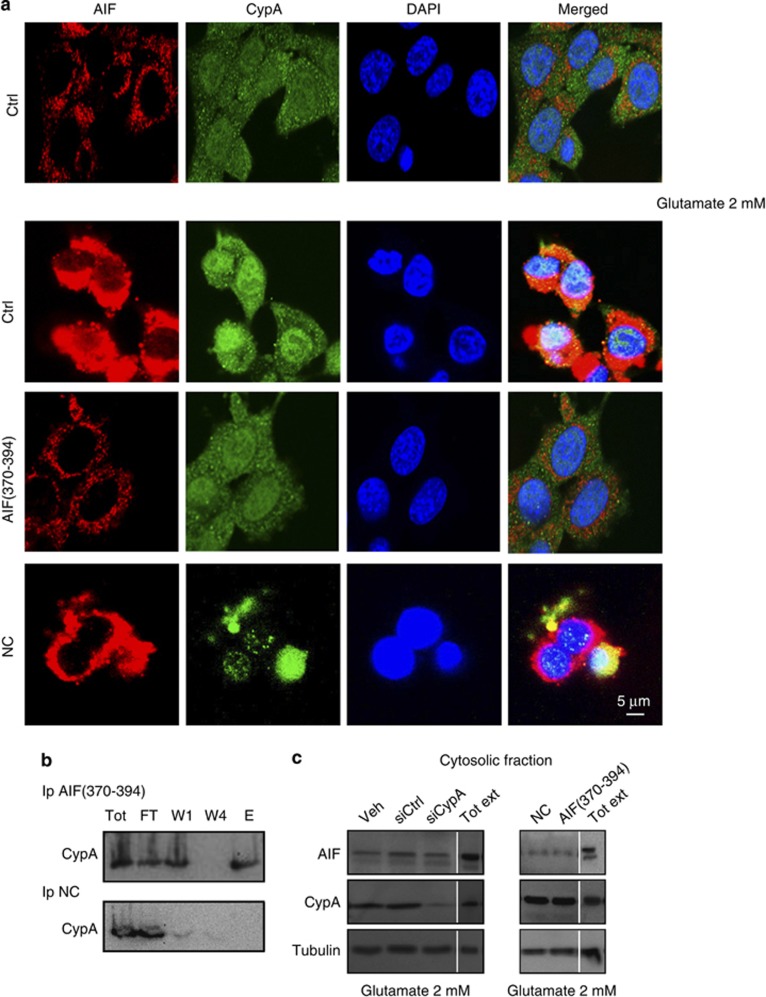
Figure 5.
AIF(370–394) delivery abrogates the nuclear translocation of AIF. To see whether the CypA-binding peptide could block translocation of both proteins following glutamate treatment, HT-22 cells were transiently transfected with 50 μM of either AIF(370–394) or NC and then exposed to 2 mM glutamate or control buffer for 12 h. Following immunostaining for AIF and CypA and examination by confocal microscopy, we found that only AIF(370–394) at the indicated concentration effectively prevented nuclear translocation of both proteins. (b) Immunoprecipitation experiments of AIF(370–394) and CypA in HT-22 cells. After immobilization of peptides on the resins and their incubation of HT-22 total extracts, the immunodetection of CypA, we found that CypA was captured only by AIF(370–394) (upper panel, lane E) peptide and not by NC (lower panel, lane E); (c) Cytosolic fraction recovered from wt, AIF(370–394) and siCypA transfected HT-22 cells after glutamate treatment in a range of 12–14 h were blotted for AIF detection. Compared with the cytosolic level of AIF in control cells (Veh, siCtrl, NC), glutamate treatment does not induce a significant increase of AIF in the cytosol