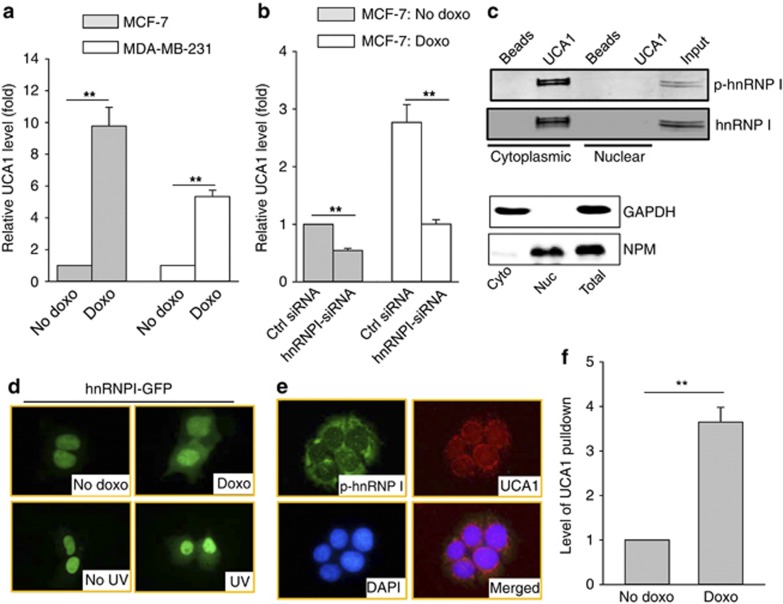
Figure 3.
Induction of UCA1 through interaction with hnRNP I. (a) Doxo induces UCA1 independent of p53, as detected by qRT–PCR in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Cells were treated with doxo at 1 μg/ml for 24 h before they were harvested for RNA extraction. (b) Suppression of doxo-induced UCA1 by hnRNP I-siRNA. MCF-7 cells were first transfected with control siRNA or hnRNP I-siRNA and then treated with doxo at 1 μg/ml for 24 h before they were harvested for RNA extraction. (c) The phosphorylated form of hnRNP I is localized in the cytoplasm and is responsible for interaction with UCA1. RNA precipitation was used to detect hnRNP I. The same membrane was probed simultaneously with hnRNP I antibody (mouse origin) and p-hnRNP I antibody (rabbit origin), followed by secondary antibody labeled with either IRDye 680 or IRDye 800. The bottom panel shows the cytoplasmic (cyto) and nuclear (nuc) extracts used for RNA precipitation assays in the top panels. GAPDH serves as a cytoplasmic marker and NPM as a nuclear marker. (d) Redistribution of hnRNP I in response to doxo treatment. MCF-7 cells were first transfected with GFP–hnRNP I fusion construct, followed by doxo treatment (1 μg/ml) for 8 h or UV treatment (20 J/m2) for 3 h before fixation for fluorescent microscopy. (e) Colocalization of phosphorylated hnRNP I with UCA1 by IF and fluorescence in situ hybridization. (f) Doxo increases UCA1 pulldown by hnRNP I antibody. MCF-7 cells were treated with doxo the same way as in d, and then cytoplasmic fraction was prepared for RIP assay. Error bars represent S.E.M., n=3. **P<0.01