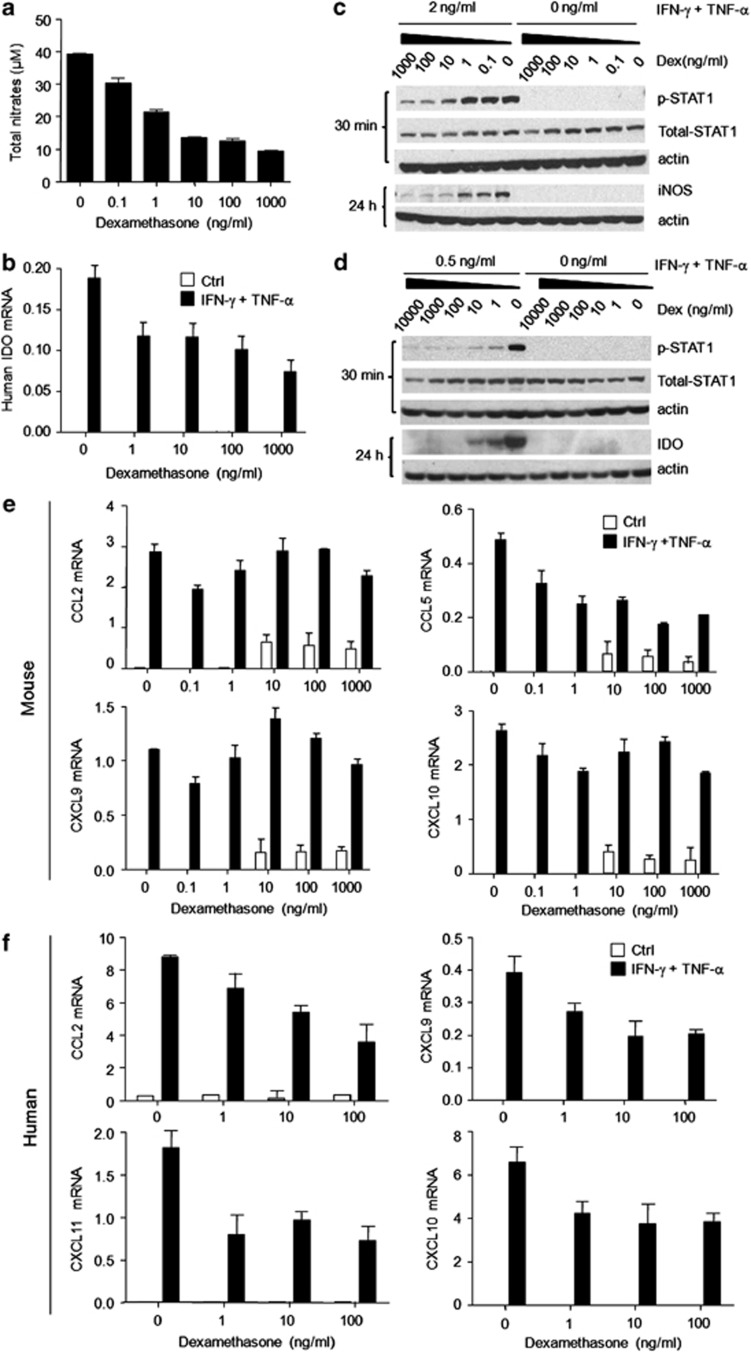
Figure 2.
Dex blocked the expression of inflammatory cytokine-induced iNOS and IDO through inhibiting STAT1 phosphorylation. Cultured mouse MSCs or human MSCs were supplemented with the indicated combinations of IFN-γ and TNF-α (10 ng/ml each), with or without Dex for 24 h. (a) Nitrates were assayed in mouse MSC supernatants. (b) IDO mRNA in human MSCs was determined using real-time PCR. (c) Cultured mouse MSCs were supplemented with IFN-γ and TNF-α (2 ng/ml each), and graded dosages of Dex. STAT1 phosphorylation and iNOS expression at 30 min and 24 h were detected by western blot analysis. (d) Similarly, human MSCs were supplemented with IFN-γ and TNF-α (0.5 ng/ml each) with or without Dex. STAT1 phosphorylation and IDO expression at 30 min and 24 h were examined. (e) Mouse MSCs were stimulated with IFN-γ and TNF-α (10 ng/ml each) for 12 h, in the presence of graded doses of Dex. Levels of mRNA for CCL2, CCL5, CXCL9, and CXCL10 were detected and normalized to β-actin. (f) Similarly, CCL2, CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11 mRNA were detected in human MSCs, after stimulation with IFN-γ and TNF-α (10 ng/ml each) for 12 h in the presence of graded doses of Dex. Values are shown as mean±S.E.M. Representative of four independent experiments