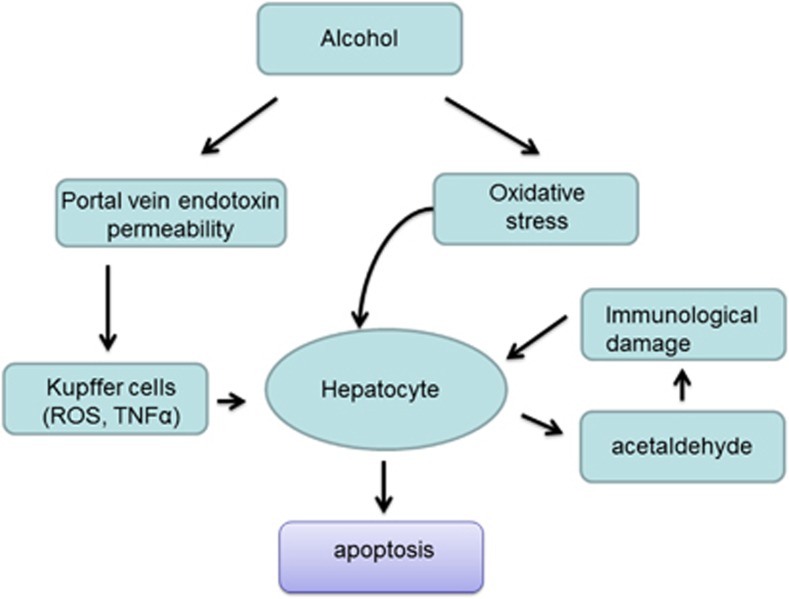
Figure 4.
Signaling mechanism of alcoholic liver injury. Oxidative stress is an important mechanism in alcoholic liver disease. Moreover, alcohol increases levels of bacterial endotoxin in the liver, which further activates liver Kupffer cells to produce inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNFα) and/or chemokines (e.g., IL-8). The acetaldehyde interacts with proteins in the liver, forming compounds called adducts that can additionally activate certain immune cells to produce various cytokines, including interleukins, IFNγ, and TNFα. All of these diverse pathways contribute to the induction of apoptosis and organ damage