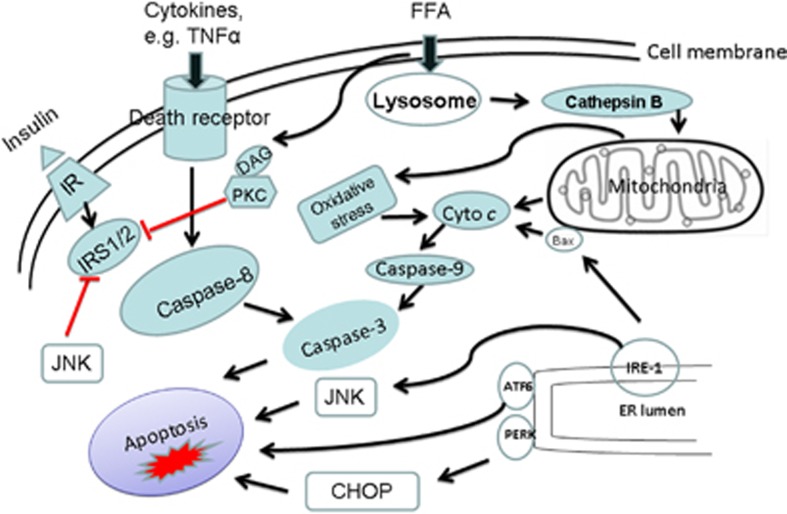
Figure 6.
Possible pathways of fat-induced hepatic apoptosis. The distinct mediators of fatty liver disease may include circulating cytokines, adipokines, and free fatty acids (FFAs). Peripheral insulin resistance enhances the delivery of FFAs to the liver, resulting in an imbalance of FFA metabolism and synthesis, thus promoting hepatic steatosis. Steatotic livers increase inflammatory cytokines, ROS, and ER stress, which trigger apoptotic cascade. Insulin sensitivity is further impaired by JNK-mediated phosphorylation of IRS1 and 2. Moreover, adipocytokines such as leptin and adiponectin are regulated by levels of circulating cytokine such as TNFα