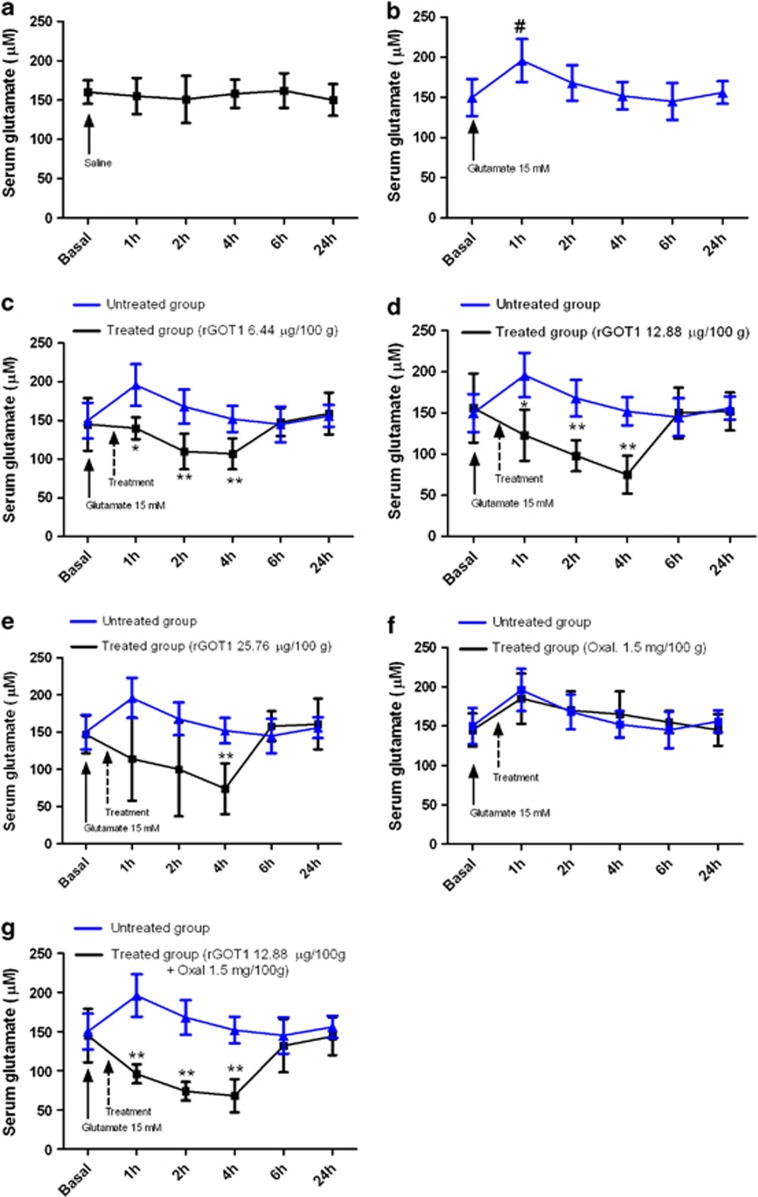
Figure 1.
Effect of rGOT and oxaloacetate (Oxal) on serum glutamate levels in healthy rats. Glutamate 15 mM was injected i.v. 30 min prior to treatments. (a) Rats treated with saline (control group). (b) Rats treated with glutamate 15 mM. (c) Comparison between rats treated with glutamate 15 mM (blue line) and rats treated with glutamate 15 mM and rGOT1 6.44 μg per 100 g (black line). (d) Comparison between rats treated with glutamate 15 mM (blue line) and rats treated with glutamate 15 mM and rGOT1 12.88 μg per 100 g (black line). (e) Comparison between rats treated with glutamate (15 mM) (blue line) and rats treated with glutamate (15 mM) and with rGOT1 (25.76 μg per 100 g). (f) Comparison between rats treated with glutamate 15 mM (blue line) and rats treated with glutamate (15 mM) and oxaloacetate (Oxal) (1.5 mg per 100 g). (g) Comparison between rats treated with glutamate (15 mM) (blue line) and rats treated with glutamate (15 mM) and rGOT1 (12.88 μg per 100 g) plus oxaloacetate (Oxal) (1.5 mg per 100 g). Solid arrows denote the injection of glutamate. Dashed arrows indicate the injection of treatments. Serum samples were taken in basal conditions and 1, 2, 4, 6 and 24 h after glutamate injection. Data are shown as mean±S.E.M. #P<0.05 compared to the basal levels; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with animals treated with glutamate 15 mM