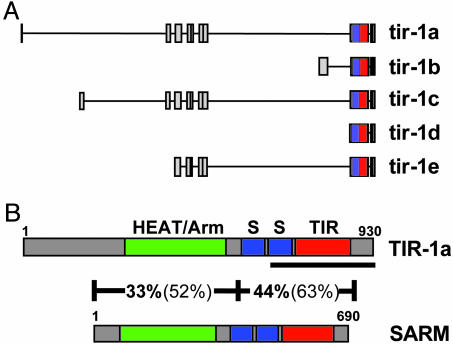
Fig. 4.
(A) Genomic structure of five known isoforms of tir-1 (see the WormBase web site, www.wormbase.org, Release WS115). Each box represents an individual exon. Each line represents intronic DNA. Note that each isoform includes exon 8, which encodes both the SAM domains (blue) and the TIR domain (red). (B) Domain architecture of the C. elegans TIR-1A and H. sapiens SARM proteins. SAM domains (S, blue), TIR domains (red), and HEAT/Armadillo repeats (green) are denoted in the figure. The amino acid length of each protein is noted. Results of blastp analysis of two different sections of the TIR-1 and SARM protein sequences are shown. Percentage amino acid identity is shown in bold, and percentage amino acid homology is shown in parentheses. Additional HEAT/Armadillo repeats overlap the SAM and TIR domains but were omitted from the figure for the sake of clarity. The TIR-1 protein encoded by the gene sequence targeted by the RNAi clone used in this study is underlined. Note that this RNAi-targeted gene segment includes the TIR domain. Because the region of the tir-1 gene targeted by RNA interference is shared among all TIR-1 isoforms, the expression of each isoform was inhibited by this treatment.