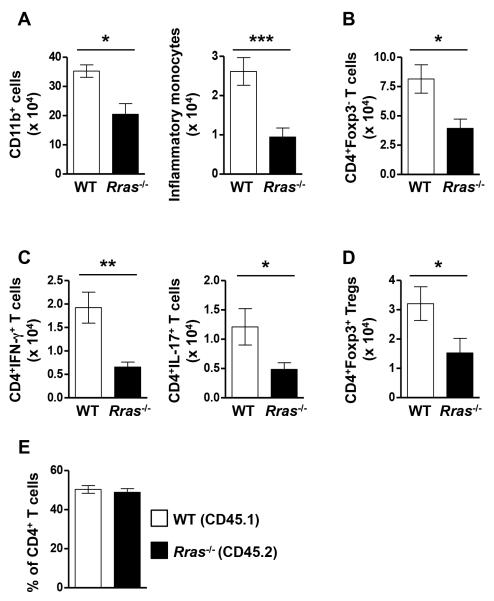
Figure 2. The absolute number of CD11b+ cells, CD4+ T cells and those producing IFN-γ or IL-17 are reduced in the CNS of Rras−/− mice during EAE.
A-E, EAE was induced in WT and Rras−/− mice at 6-8 wk of age by immunization with MOG35-55 peptide. A-D, CNS mononuclear cells were isolated 17 days after EAE induction and the absolute number of total myeloid cells (CD11b+) (A), inflammatory monocytes (CD11b+Ly6C+CCR2+) (A), effector CD4 T cells (CD4+Foxp3−) (B), IFN-γ and IL-17 producing CD4+ cells (C) and Treg (CD4+Foxp3+) (D) were determined by flow cytometry. Pooled data from three (A-C) or four (D) independent experiments with nine (A,B), 8-9 (C) or 12 (D) total mice in each group are shown. E, lethally irradiated WT mice were transplanted with an equal mix of CD45.1+ WT and CD45.2+ Rras−/− BM cells to generate mixed BM chimera mice. Ten weeks after BM reconstitution, EAE was induced by immunization with MOG35-55 peptide. At the peak of EAE disease, the percentages of WT (CD45.1+) and Rras−/− (CD45.2+) cells amongst CNS infiltrating effector T cells (CD4+Foxp3−) was determined. Pooled data from 2 independent experiments with eight mice in each group are shown. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.