Figure 7. PAR2 activation promotes Ca2+-dependent NFAT translocation and TSLP secretion.
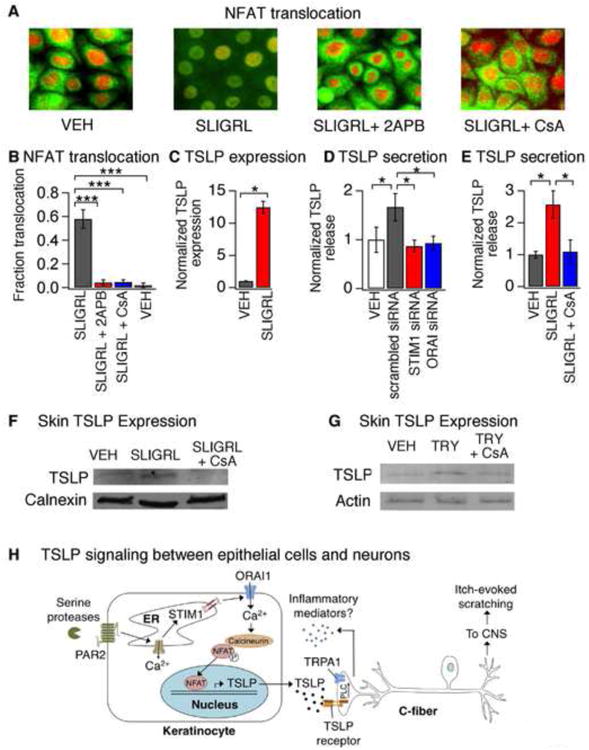
(A) Representative images displaying cytosolic and nuclear localization of NFAT (green) and DAPI (red) in keratinocytes after a 30 min incubation with vehicle (VEH), SLIGRL (100μM), SLIGRL + 2APB (50μM) or SLIGRL + CsA (1μM). Pretreatment with 2APB or CsA prevented SLIGRL-induced NFAT nuclear translocation. n≥300 cells. (B) Fraction of HaCaT keratinocytes displaying nuclear localization of NFAT-GFP following treatment with SLIGRL (100μM; black), SLIGRL and 2APB (50 μM; red), SLIGRL + CsA (1μM; blue) or vehicle (VEH; white). n≥1000 cells. (C) TSLP expression in human keratinocytes following a 3h treatment with vehicle (VEH, black) or SLIGRL (100μM, red). n≥3. (D) SLIGRL-evoked TSLP release in cells treated with scrambled (black), STIM1 (red) or ORAI1 siRNA (blue). Secretion was normalized to vehicle-treated cells (white). n≥3. (E) TSLP release in response to treatment with vehicle (VEH, black), SLIGRL (100 μM, red) or SLIGRL + CsA (1μM, blue). (F) Western blot of skin lysates from mice following intradermal injection with vehicle (VEH), SLIGRL, or SLIGRL+CsA. Samples were probed with antibodies against TSLP and calnexin (loading control). n≥3 mice. (G) Western blot of skin lysates isolated from mice following intradermal injection with vehicle (VEH), tryptase (TRY; 100pg/20μL), or tryptase+CsA (TRY + CsA). Samples were probed with antibodies against TSLP, and actin (loading control). n≥3 mice. *P<0.05; **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Error bars represent s.e.m. (H) Schematic diagram depicting the ORAI1 signaling pathway in keratinocytes that links PAR2 to TSLP secretion and activation of itch neurons. Activation of PAR2 triggers release of Ca2+ from the ER and activation of STIM1, which opens ORAI1 channels to promote Ca2+ influx. Ca2+ activates the phosphatase calcineurin, which dephosphorylates NFAT and causes nuclear translocation, thus inducing transcription of TSLP. Secreted TSLP depolarizes a subset of C-fibers to evoke itch, in a TSLPR- and TRPA1-dependent manner. Activation of TRPA1-expressing sensory neurons can then lead to release of neuropeptides in the skin in a process known as neurogenic inflammation.
