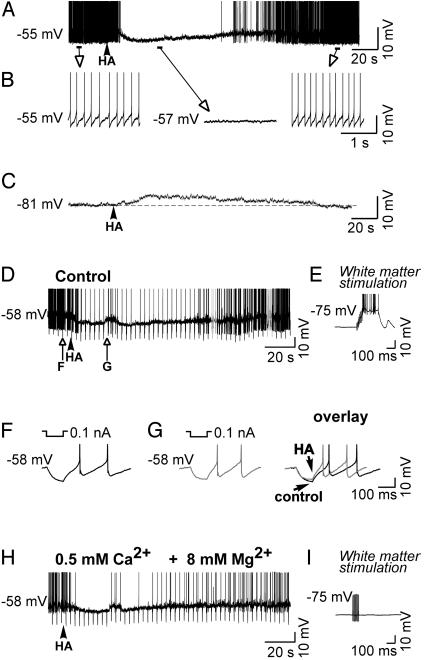
Fig. 1.
HA hyperpolarizes and inhibits tonic action potential activity in perigeniculate GABAergic neurons. (A) Local application of HA results in a slow membrane hyperpolarization and inhibition of tonic action potential activity. (B) Expansion of portions of the recording in A.(C) Application of HA while the neuron was hyperpolarized to -81 mV resulted in a slow membrane depolarization. (D) Response of another PGN cell to the local application of HA, again illustrating the hyperpolarizing, inhibitory response. (E) Response to an orthodromic stimulus of the optic radiation illustrating intact synaptic transmission. (F and G) Expansion of the response to hyperpolarizing current pulses before and after application of HA, illustrating the small decrease in apparent input resistance during the prolonged hyperpolarization. (H) Block of synaptic transmission through bath application of high Mg2+ (8 mM) and low Ca2+ (0.5 mM). This manipulation failed to block the HA-induced hyperpolarization and decrease in apparent input conductance. (I) Response to an orthodromic stimulus of the optic radiation was abolished completely, indicating that normal synaptic transmission was blocked by the high Mg2+, low Ca2+ solution.